Intravesical foreign body-induced bladder calculi resulting in obstructive renal failure
- PMID: 18953457
- PMCID: PMC2572241
- DOI: 10.5489/cuaj.927
Intravesical foreign body-induced bladder calculi resulting in obstructive renal failure
Abstract
We report the case of a 30-year-old man who presented with obstructive renal failure and urosepsis due to bladder outlet-obstructing bladder calculi that formed around 3 copper wires that were self-inserted into his urinary bladder 15 years previously. We present the evaluation, imaging and management of the unique complications resulting from the self-insertion of an intra-vesical foreign body. Our patient's case was unique for 2 reasons. First, the length of time (15 yr) from foreign body insertion to presentation is the longest interval reported in the literature. Second, this is the first report of bladder calculi induced by the insertion of a foreign body that resulted in obstructive renal failure.
Figures
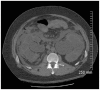
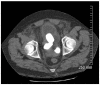


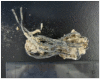
References
-
- Loeser A, Gerharz EW, Riedmiller H. Chronic perforation of the urinary bladder by self-inserted foreign body. Int Urogynecol J Pelvic Floor Dysfunct. 2007;18:689–90. - PubMed
-
- Kenney RD. Adolescent males who insert genitourinary foreign bodies: Is psychiatric referral required? Urology. 1988;32:127–9. - PubMed
-
- Costa G, Di Tonno F, Capodieci S, et al. Self-introduction of foreign bodies into the urethra: a multidisciplinary problem. Int Urol Nephrol. 1993;25:77–81. - PubMed
-
- Bartoletti R, Gacci M, Travaglini F, et al. Intravesical migration of AMS 800 artificial urinary sphincter and stone formation in a patient who underwent radical prostatectomy. Urol Int. 2000;64:167–8. - PubMed
-
- Huang WC, Yang JM. Sonographic appearance of a bladder calculus secondary to a suture from a bladder neck suspension. J Ultrasound Med. 2002;21:1303–5. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
