Gene expression profiling of breast cancer
- PMID: 18953822
- PMCID: PMC2775529
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yasu.2008.03.002
Gene expression profiling of breast cancer
Abstract
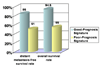
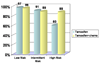
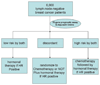
Gene expression profiling is enabling scientists to understand the heterogeneous nature of breast cancer on a genomic level. Several gene expression profiles for breast cancers have emerged in the initial studies and appear to be generally concordant in their ability to predict poor outcome. Of these profiles, the Oncotype Dx and Mammaprint assays are the best validated and are commercially available. Their role in clinical practice is being refined through ongoing clinical trials. Other efforts are directed at determining host factors that might help identify prognosis as well as response and toxicity of therapy. It is expected that availability of these types of analyses will only increase in the future. It will be imperative that such assays be well validated and have implications for how to modify care for the individual patient.
Figures

References
-
- van't Veer LJ, Paik S, Hayes DF. Gene expression profiling of breast cancer: a new tumor marker. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:1631–1635. - PubMed
-
- Lipshutz RJ, Morris D, Chee M, et al. Using oligonucleotide probe arrays to access genetic diversity. Biotechniques. 1995;19:442–447. - PubMed
-
- Schena M, Shalon D, Davis RW, Brown PO. Quantitative monitoring of gene expression patterns with a complementary DNA microarray. Science. 1995;270:467–470. - PubMed
-
- Quackenbush J. Microarray analysis and tumor classification. N Engl J Med. 2006;354:2463–2472. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

