A new cross-talk between the aryl hydrocarbon receptor and RelB, a member of the NF-kappaB family
- PMID: 18955032
- PMCID: PMC2688397
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bcp.2008.09.036
A new cross-talk between the aryl hydrocarbon receptor and RelB, a member of the NF-kappaB family
Abstract
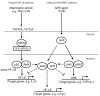
The discovery of the new crosstalk between the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) and the NF-kappaB subunit RelB may extend our understanding of the biological functions of the AhR and at the same time raises a number of questions, which will be addressed in this review. The characteristics of this interaction differ from that of AhR with RelA in that the latter appears to be mostly negative unlike the collaborative interactions of AhR/RelB. The AhR/RelB dimer is capable of binding to DNA response elements including the dioxin response element (DRE) as well as NF-kappaB binding sites supporting the activation of target genes of the AhR as well as NF-kappaB pathway. Further studies show that AhR/RelB complexes can be found not only in lymphoid cells but also in a human hepatoma cell line (HepG2) or breast cancer cell line (MDA-MB-231). RelB has been implicated in carcinogenesis of breast cancer for instance and RelB is known to be a critical factor for the function and differentiation of dendritic cells; interestingly the participation of AhR in both processes has been suggested recently, which offers the great potential to expand the scope of the physiological roles of the AhR. There is evidence indicating that RelB may serve as a pro-survival factor, including its ability to promote "inflammation resolution" besides the association of RelB with inflammatory disorders. Based on such information, a hypothesis has been proposed in this review that AhR together with RelB functions as a coordinator of inflammatory responses.
Figures



References
-
- Gu YZ, Hogenesch JB, Bradfield CA. The PAS superfamily: sensors of environmental and developmental signals. Ann Rev Pharmacol and Toxicol. 2000;40:519–61. - PubMed
-
- Denison MS, Nagy SR. Activation of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor by structurally diverse exogenous and endogenous chemicals. Ann Rev Pharmacol and Toxicol. 2003;43:309–34. - PubMed
-
- Rannug A, Rannug U, Rosenkranz HS, Winqvist L, Westerholm R, Agurell E, et al. Certain photooxidized derivatives of tryptophan bind with very high affinity to the Ah receptor and are likely to be endogenous signal substances. J Biol Chem. 1987;262:15422–7. - PubMed
-
- Singh SS, Hord NG, Perdew GH. Characterization of the activated form of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor in the nucleus of HeLa cells in the absence of exogenous ligand. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1996;329:47–55. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

