Electroacupuncture of 2 hz has a rewarding effect: evidence from a conditioned place preference study in rats
- PMID: 18955347
- PMCID: PMC3163068
- DOI: 10.1093/ecam/nen043
Electroacupuncture of 2 hz has a rewarding effect: evidence from a conditioned place preference study in rats
Abstract
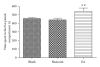
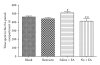
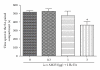
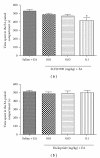
Electroacupuncture (EA) has been used to suppress heroin craving in addicts and the conditioned place preference (CPP) for morphine in the rat. The question remained whether EA by itself will produce some rewarding effect. This was investigated using the CPP procedure in the present study. The results indicated that rats showed a significant preference to the 2 Hz EA-paired compartment. This rewarding effect of EA was prevented by pre-treatment with the opioid receptor antagonist naloxone [2 mg kg(-1), intraperitoneally (i.p.)], CB1 cannabinoid antagonist AM251 (3 μg per rat, intracerebroventricularly) or D1 dopamine receptor antagonist SCH23390 (0.1 mg kg(-1), i.p.), respectively. TempspacetempspaceIt is concluded that 2 Hz EA is capable of inducing CPP in the rat via the activation of the endogenous opioid-, cannabinoid- and dopamine-systems.
Figures
References
-
- Ulett GA, Han S, Han J-S. Electroacupuncture: mechanisms and clinical application. Biological Psychiatry. 1998;44(2):129–138. - PubMed
-
- Chen XH, Han JS. Analgesia induced by electroacupuncture of different frequencies is mediated by different types of opioid receptors: another cross-tolerance study. Behavioural Brain Research. 1992;47:143–149. - PubMed
-
- Han JS, Wu LZ, Cui CL. Herion addicts treated with transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation of identified frequencies. Regulatory Peptides. 1994;54:115–116.
-
- Wang B, Zhang BG, Ge X, Luo F, Han JS. Inhibition by peripheral electric stimulation of the reinstatement of morphine-induced place preference in rats and drug-craving in heroin addicts. Journal of Peking University (Health Sciences) 2003;85:241–247. - PubMed
-
- Wu LZ, Cui CL, Han JS. 2/100 Hz transcutaneous electrical stimulation for the treatment of heroine addiction. Journal of Beijing Medical University. 1999;31:239–242.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

