Human basophils and eosinophils are the direct target leukocytes of the novel IL-1 family member IL-33
- PMID: 18955562
- PMCID: PMC2644080
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2008-05-157818
Human basophils and eosinophils are the direct target leukocytes of the novel IL-1 family member IL-33
Abstract
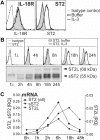
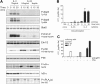
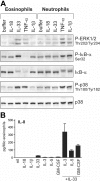
In mice, interleukin-18 (IL-18) regulates Th1- or Th2-type immune responses depending on the cytokine environment and effector cells involved, and the ST2-ligand, IL-33, primarily promotes an allergic phenotype. Human basophils, major players in allergic inflammation, constitutively express IL-18 receptors, while ST2 surface expression is inducible by IL-3. Unexpectedly, freshly isolated basophils are strongly activated by IL-33, but, in contrast to mouse basophils, do not respond to IL-18. IL-33 promotes IL-4, IL-13 and IL-8 secretion in synergy with IL-3 and/or FcepsilonRI-activation, and enhances FcepsilonRI-induced mediator release. These effects are similar to that of IL-3, but the signaling pathways engaged are distinct because IL-33 strongly activates NF-kappaB and shows a preference for p38 MAP-kinase, while IL-3 acts through Jak/Stat and preferentially activates ERK. Eosinophils are the only other leukocyte-type directly activated by IL-33, as evidenced by screening of p38-activation in peripheral blood cells. Only upon CD3/CD28-ligation, IL-33 weakly enhances Th2 cytokine expression by in vivo polarized Th2 cells. This study on primary human cells demonstrates that basophils and eosinophils are the only direct target leukocytes for IL-33, suggesting that IL-33 promotes allergic inflammation and Th2 polarization mainly by the selective activation of these specialized cells of the innate immune system.
Figures


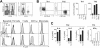
Comment in
-
Interleukin-33: a regulator of basophils.Blood. 2009 Feb 12;113(7):1396-7. doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-11-189811. Blood. 2009. PMID: 19221042
References
-
- Martin MU, Wesche H. Summary and comparison of the signaling mechanisms of the Toll/interleukin-1 receptor family. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002;1592:265–280. - PubMed
-
- Dinarello CA. The IL-1 family and inflammatory diseases. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2002;20(5) suppl 27:S1–13. - PubMed
-
- Wilson NJ, Boniface K, Chan JR, et al. Development, cytokine profile and function of human interleukin 17-producing helper T cells. Nat Immunol. 2007;8:950–957. - PubMed
-
- Acosta-Rodriguez EV, Napolitani G, Lanzavecchia A, Sallusto F. Interleukins 1beta and 6 but not transforming growth factor-beta are essential for the differentiation of interleukin 17-producing human T helper cells. Nat Immunol. 2007;8:942–949. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

