Targeting the leukemia microenvironment by CXCR4 inhibition overcomes resistance to kinase inhibitors and chemotherapy in AML
- PMID: 18955566
- PMCID: PMC2699240
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2008-05-158311
Targeting the leukemia microenvironment by CXCR4 inhibition overcomes resistance to kinase inhibitors and chemotherapy in AML
Abstract
SDF-1alpha/CXCR4 signaling plays a key role in leukemia/bone marrow microenvironment interactions. We previously reported that bone marrow-derived stromal cells inhibit chemotherapy-induced apoptosis in acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Here we demonstrate that the CXCR4 inhibitor AMD3465 antagonized stromal-derived factor 1alpha (SDF-1alpha)-induced and stroma-induced chemotaxis and inhibited SDF-1alpha-induced activation of prosurvival signaling pathways in leukemic cells. Further, CXCR4 inhibition partially abrogated the protective effects of stromal cells on chemotherapy-induced apoptosis in AML cells. Fetal liver tyrosine kinase-3 (FLT3) gene mutations activate CXCR4 signaling, and coculture with stromal cells significantly diminished antileukemia effects of FLT3 inhibitors in cells with mutated FLT3. Notably, CXCR4 inhibition increased the sensitivity of FLT3-mutated leukemic cells to the apoptogenic effects of the FLT3 inhibitor sorafenib. In vivo studies demonstrated that AMD3465, alone or in combination with granulocyte colony-stimulating factor, induced mobilization of AML cells and progenitor cells into circulation and enhanced antileukemic effects of chemotherapy and sorafenib, resulting in markedly reduced leukemia burden and prolonged survival of the animals. These findings indicate that SDF-1alpha/CXCR4 interactions contribute to the resistance of leukemic cells to signal transduction inhibitor- and chemotherapy-induced apoptosis in systems mimicking the physiologic microenvironment. Disruption of these interactions with CXCR4 inhibitors represents a novel strategy of sensitizing leukemic cells by targeting their protective bone marrow microenvironment.
Figures

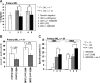
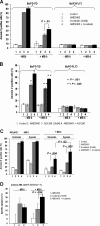
 , ■) were treated with 3 μM ara-C for 24 hours. The percentage of the apoptotic cells (annexin V–positive cells) were analyzed by flow cytometry. (C) AMD3465 sensitized primary AML cells (n = 20) cocultured with stromal MS-5 cells to ara-C–induced apoptosis (24 hours). Apoptotic cells were detected by annexin V flow cytometry after gating on CD34+ leukemic cells. The specific apoptosis was calculated by the formula: % specific apoptosis = (test – control) × 100/(100 – control).
, ■) were treated with 3 μM ara-C for 24 hours. The percentage of the apoptotic cells (annexin V–positive cells) were analyzed by flow cytometry. (C) AMD3465 sensitized primary AML cells (n = 20) cocultured with stromal MS-5 cells to ara-C–induced apoptosis (24 hours). Apoptotic cells were detected by annexin V flow cytometry after gating on CD34+ leukemic cells. The specific apoptosis was calculated by the formula: % specific apoptosis = (test – control) × 100/(100 – control).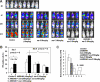
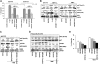
Comment in
-
Another nail in the AML coffin.Blood. 2009 Jun 11;113(24):6045-6. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-03-189803. Blood. 2009. PMID: 19520813 No abstract available.
References
-
- Wilson A, Trumpp A. Bone-marrow haematopoietic-stem-cell niches. Nat Rev Immunol. 2006;6:93–106. - PubMed
-
- Taylor ST, Hickman JA, Dive C. Epigenetic determinants of resistance to etoposide regulation of Bcl-X(L) and Bax by tumor microenvironmental factors. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2000;92:18–23. - PubMed
-
- Tabe Y, Konopleva M, Munsell MF, et al. PML-RARα is associated with leptin-receptor induction: the role of mesenchymal stem cell-derived adipocytes in APL cell survival. Blood. 2004;103:1815–1822. - PubMed
-
- Panayiotidis P, Jones D, Ganeshaguru K, Foroni L, Hoffbrand AV. Human bone marrow stromal cells prevent apoptosis and support the survival of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia cells in vitro. Br J Haematol. 1996;92:97–103. - PubMed
-
- Vincent AM, Cawley JC, Burthem J. Integrin function in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood. 1996;87:4780–4788. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

