Distribution, abundance and diversity of the extremely halophilic bacterium Salinibacter ruber
- PMID: 18957079
- PMCID: PMC2596770
- DOI: 10.1186/1746-1448-4-15
Distribution, abundance and diversity of the extremely halophilic bacterium Salinibacter ruber
Abstract
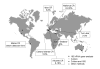
Since its discovery in 1998, representatives of the extremely halophilic bacterium Salinibacter ruber have been found in many hypersaline environments across the world, including coastal and solar salterns and solar lakes. Here, we review the available information about the distribution, abundance and diversity of this member of the Bacteroidetes.
Figures



References
-
- Benlloch S, Martínez-Murcia AJ, Rodríguez-Valera F. Sequencing of bacterial and archaeal 16S rRNA genes directly amplified from a hypersaline environment. Syst Appl Microbiol. 1995;18:574–581.
-
- Martínez-Murcia AJ, Acinas SG, Rodríguez-Valera F. Evaluation of prokaryotic diversity by restrictase digestion of 16S rDNA directly amplified from hypersaline environments. FEMS Microb Ecol. 1995;17:247–256.
-
- Antón J, Oren A, Benlloch S, Rodríguez-Valera F, Amann R, Rosselló-Mora R. Salinibacter ruber gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel, extreme halophilic member of the Bacteria from saltern crystallizer ponds. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2002;52:485–491. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

