Hmga2 promotes neural stem cell self-renewal in young but not old mice by reducing p16Ink4a and p19Arf Expression
- PMID: 18957199
- PMCID: PMC2582221
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.09.017
Hmga2 promotes neural stem cell self-renewal in young but not old mice by reducing p16Ink4a and p19Arf Expression
Abstract
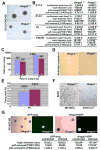
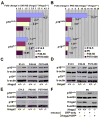
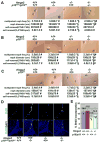
Stem cells persist throughout life in diverse tissues by undergoing self-renewing divisions. Self-renewal capacity declines with age, partly because of increasing expression of the tumor suppressor p16(Ink4a). We discovered that the Hmga2 transcriptional regulator is highly expressed in fetal neural stem cells but that expression declines with age. This decrease is partly caused by the increasing expression of let-7b microRNA, which is known to target HMGA2. Hmga2-deficient mice show reduced stem cell numbers and self-renewal throughout the central and peripheral nervous systems of fetal and young-adult mice but not old-adult mice. Furthermore, p16(Ink4a) and p19(Arf) expression were increased in Hmga2-deficient fetal and young-adult stem cells, and deletion of p16(Ink4a) and/or p19(Arf) partially restored self-renewal capacity. let-7b overexpression reduced Hmga2 and increased p16(Ink4a)/p19(Arf) expression. Hmga2 thus promotes fetal and young-adult stem cell self-renewal by decreasing p16(Ink4a)/p19(Arf) expression. Changes in let-7 and Hmga2 expression during aging contribute to the decline in neural stem cell function.
Figures




Comment in
-
Ink4a/Arf regulation by let-7b and Hmga2: a genetic pathway governing stem cell aging.Cell Stem Cell. 2008 Nov 6;3(5):469-70. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2008.10.008. Cell Stem Cell. 2008. PMID: 18983959
-
HMGA2, microRNAs, and stem cell aging.Cell. 2008 Dec 12;135(6):1013-6. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.11.026. Cell. 2008. PMID: 19070572 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Arlotta P, Tai AK, Manfioletti G, Clifford C, Jay G, Ono SJ. Transgenic mice expressing a truncated form of the high mobility group I-C protein develop adiposity and an abnormally high prevalence of lipomas. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:14394–14400. - PubMed
-
- Benson KF, Chada K. Mini-mouse: phenotypic characterization of a transgenic insertional mutant allelic to pygmy. Genet Res. 1994;64:27–33. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

