Cytokine-induced signaling networks prioritize dynamic range over signal strength
- PMID: 18957207
- PMCID: PMC2635014
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.08.034
Cytokine-induced signaling networks prioritize dynamic range over signal strength
Abstract
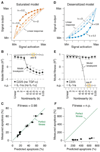
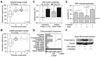
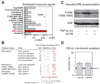
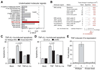
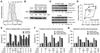
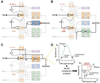
Signaling networks respond to diverse stimuli, but how the state of the signaling network is relayed to downstream cellular responses is unclear. We modeled how incremental activation of signaling molecules is transmitted to control apoptosis as a function of signal strength and dynamic range. A linear relationship between signal input and response output, with the dynamic range of signaling molecules uniformly distributed across activation states, most accurately predicted cellular responses. When nonlinearized signals with compressed dynamic range relay network activation to apoptosis, we observe catastrophic, stimulus-specific prediction failures. We develop a general computational technique, "model-breakpoint analysis," to analyze the mechanism of these failures, identifying new time- and stimulus-specific roles for Akt, ERK, and MK2 kinase activity in apoptosis, which were experimentally verified. Dynamic range is rarely measured in signal-transduction studies, but our experiments using model-breakpoint analysis suggest it may be a greater determinant of cell fate than measured signal strength.
Figures

References
-
- Albeck JG, MacBeath G, White FM, Sorger PK, Lauffenburger DA, Gaudet S. Collecting and organizing systematic sets of protein data. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2006;7:803–812. - PubMed
-
- Ballif BA, Blenis J. Molecular mechanisms mediating mammalian mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) kinase (MEK)-MAPK cell survival signals. Cell Growth Differ. 2001;12:397–408. - PubMed
-
- Blume-Jensen P, Hunter T. Oncogenic kinase signalling. Nature. 2001;411:355–365. - PubMed
-
- Campbell KJ, Rocha S, Perkins ND. Active repression of antiapoptotic gene expression by RelA(p65) NF-kappa B. Mol Cell. 2004;13:853–865. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

