Structural insights into G-protein-coupled receptor activation
- PMID: 18957321
- PMCID: PMC4019673
- DOI: 10.1016/j.sbi.2008.09.010
Structural insights into G-protein-coupled receptor activation
Abstract
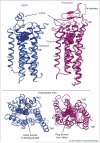
G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) are the largest family of eukaryotic plasma membrane receptors, and are responsible for the majority of cellular responses to external signals. GPCRs share a common architecture comprising seven transmembrane (TM) helices. Binding of an activating ligand enables the receptor to catalyze the exchange of GTP for GDP in a heterotrimeric G protein. GPCRs are in a conformational equilibrium between inactive and activating states. Crystallographic and spectroscopic studies of the visual pigment rhodopsin and two beta-adrenergic receptors have defined some of the conformational changes associated with activation.
Figures


References
-
- Kobilka BK, Deupi X. Conformational complexity of G-protein-coupled receptors. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2007;28:397–406. - PubMed
-
- Krebs A, Villa C, Edwards PC, Schertler GF. Characterisation of an improved two-dimensional p22121 crystal from bovine rhodopsin. J Mol Biol. 1998;282:991–1003. - PubMed
-
- Schertler GF, Villa C, Henderson R. Projection structure of rhodopsin. Nature. 1993;362:770–772. - PubMed
-
- Palczewski K, Kumasaka T, Hori T, Behnke CA, Motoshima H, Fox BA, Le Trong I, Teller DC, Okada T, Stenkamp RE, et al. Crystal structure of rhodopsin: a G protein-coupled receptor [see comments]. Science. 2000;289:739–745. - PubMed
-
- Okada T, Le Trong I, Fox BA, Behnke CA, Stenkamp RE, Palczewski K. X-ray diffraction analysis of three-dimensional crystals of bovine rhodopsin obtained from mixed micelles. J Struct Biol. 2000;130:73–80. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

