Conditions mimicking acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction in patients referred for primary percutaneous coronary intervention
- PMID: 18958255
- PMCID: PMC2570763
- DOI: 10.1007/BF03086173
Conditions mimicking acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction in patients referred for primary percutaneous coronary intervention
Abstract
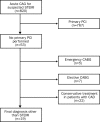
BACKGROUND/OBJECTIVES.: A rapid diagnosis of ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) is mandatory for optimal treatment. However, a small proportion of patients with suspected STEMI suffer from other conditions. Although case reports have described these conditions, a contemporary systematic analysis is lacking. We report the incidence, clinical characteristics and outcome of patients with suspected STEMI referred for primary percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) with a final diagnosis other than STEMI. METHODS.: From January 2004 to July 2005, 820 consecutive patients were included with suspected STEMI who were referred for primary PCI to a university medical centre, based on a predefined protocol. Clinical characteristics, final diagnosis and outcome were obtained from patient charts and databases. RESULTS.: In 19 patients (2.3%), a final diagnosis other than myocardial infarction was established: coronary aneurysm (n=1), (myo)pericarditis (n=5), cardiomyopathy (n=2), Brugada syndrome (n=1), aortic stenosis (n=1), aortic dissection (n=3), subarachnoidal haemorrhage (n=2), pneumonia (n=1), chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (n=1), mediastinal tumour (n=1), and peritonitis after recent abdominal surgery (n=1). These patients less often reported previous symptoms of angina (p<0.001), smoking (p<0.05) and a positive family history of cardiovascular diseases (p<0.05) than STEMI patients. Mortality at 30 days was 16%. CONCLUSION.: A 2.3% incidence of conditions mimicking STEMI was found in patients referred for primary PCI. A high clinical suspicion of conditions mimicking STEMI remains necessary. (Neth Heart J 2008;16:325-31.).
Keywords: ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction; coronary angiography; differential diagnosis; percutaneous coronary intervention.
Figures
References
-
- Bradley EH, Herrin J, Wang Y, et al. Strategies for reducing the door-to-balloon time in acute myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med 2006;355:2308-20. - PubMed
-
- Brodie BR, Stuckey TD, Wall TC, et al. Importance of time to reperfusion for 30-day and late survival and recovery of left ventricular function after primary angioplasty for acute myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol 1998;32:1312-9. - PubMed
-
- Zijlstra F, Patel A, Jones M, et al. Clinical characteristics and outcome of patients with early (<2 h), intermediate (2-4 h) and late (>4 h) presentation treated by primary coronary angioplasty or thrombolytic therapy for acute myocardial infarction. Eur Heart J 2002;23:550-7. - PubMed
-
- DeWood MA, Spores J, Notske R, et al. Prevalence of total coronary occlusion during the early hours of transmural myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med 1980;303:897-902. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
