Acquisition of growth-inhibitory antibodies against blood-stage Plasmodium falciparum
- PMID: 18958278
- PMCID: PMC2570221
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0003571
Acquisition of growth-inhibitory antibodies against blood-stage Plasmodium falciparum
Abstract
Background: Antibodies that inhibit the growth of blood-stage Plasmodium falciparum may play an important role in acquired and vaccine-induced immunity in humans. However, the acquisition and activity of these antibodies is not well understood.
Methods: We tested dialysed serum and purified immunoglobulins from Kenyan children and adults for inhibition of P. falciparum blood-stage growth in vitro using different parasite lines. Serum antibodies were measured by ELISA to blood-stage parasite antigens, extracted from P. falciparum schizonts, and to recombinant merozoite surface protein 1 (42 kDa C-terminal fragment, MSP1-42).
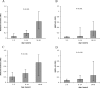
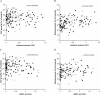
Results: Antibodies to blood-stage antigens present in schizont protein extract and to recombinant MSP1-42 significantly increased with age and were highly correlated. In contrast, growth-inhibitory activity was not strongly associated with age and tended to decline marginally with increasing age and exposure, with young children demonstrating the highest inhibitory activity. Comparison of growth-inhibitory activity among samples collected from the same population at different time points suggested that malaria transmission intensity influenced the level of growth-inhibitory antibodies. Antibodies to recombinant MSP1-42 were not associated with growth inhibition and high immunoglobulin G levels were poorly predictive of inhibitory activity. The level of inhibitory activity against different isolates varied.
Conclusions: Children can acquire growth-inhibitory antibodies at a young age, but once they are acquired they do not appear to be boosted by on-going exposure. Inhibitory antibodies may play a role in protection from early childhood malaria.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Elliott SR, Beeson JG. Estimating the burden of global mortality in children aged <5 years by pathogen-specific causes. Clin Infect Dis. 2008;46:1794–1795. - PubMed
-
- Marsh K, Kinyanjui S. Immune effector mechanisms in malaria. Parasite Immunol. 2006;28:51–60. - PubMed
-
- Cohen S, Butcher GA, Crandall RB. Action of malarial antibody in vitro. Nature. 1969;223:368–371. - PubMed
-
- Good MF, Stanisic D, Xu H, Elliott S, Wykes M. The immunological challenge to developing a vaccine to the blood stages of malaria parasites. Immunol Rev. 2004;201:254–267. - PubMed
-
- Brown GV, Anders RF, Mitchell GF, Heywood PF. Target antigens of purified human immunoglobulins which inhibit growth of Plasmodium falciparum in vitro. Nature. 1982;297:591–593. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

