Influence of the tapasin C terminus on the assembly of MHC class I allotypes
- PMID: 18958466
- PMCID: PMC2706579
- DOI: 10.1007/s00251-008-0335-x
Influence of the tapasin C terminus on the assembly of MHC class I allotypes
Abstract
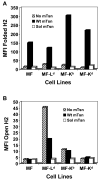
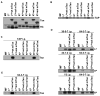
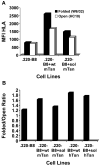
Several endoplasmic reticulum proteins, including tapasin, play an important role in major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I assembly. In this study, we assessed the influence of the tapasin cytoplasmic tail on three mouse MHC class I allotypes (H2-K(b), -K(d), and -L(d)) and demonstrated that the expression of truncated mouse tapasin in mouse cells resulted in very low K(b), K(d), and L(d) surface expression. The surface expression of K(d) also could not be rescued by human soluble tapasin, suggesting that the surface expression phenotype of the mouse MHC class I molecules in the presence of soluble tapasin was not due to mouse/human differences in tapasin. Notably, soluble mouse tapasin was able to partially rescue HLA-B8 surface expression on human 721.220 cells. Thus, the cytoplasmic tail of tapasin (either mouse or human) has a stronger impact on the surface expression of murine MHC class I molecules on mouse cells than on the expression of HLA-B8 on human cells. A K408W mutation in the mouse tapasin transmembrane/cytoplasmic domain disrupted K(d) folding and release from tapasin, but not interaction with transporter associated with antigen processing (TAP), indicating that the mechanism whereby the tapasin transmembrane/cytoplasmic domain facilitates MHC class I assembly is not limited to TAP stabilization. Our findings indicate that the C terminus of mouse tapasin plays a vital role in enabling murine MHC class I molecules to be expressed at the surface of mouse cells.
Figures
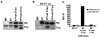
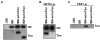
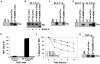
Similar articles
-
A charged amino acid residue in the transmembrane/cytoplasmic region of tapasin influences MHC class I assembly and maturation.J Immunol. 2005 Jan 15;174(2):962-9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.174.2.962. J Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15634919
-
Productive association between MHC class I and tapasin requires the tapasin transmembrane/cytosolic region and the tapasin C-terminal Ig-like domain.Mol Immunol. 2012 Jan;49(4):628-39. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2011.11.002. Epub 2011 Dec 12. Mol Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22169163 Free PMC article.
-
Soluble tapasin restores MHC class I expression and function in the tapasin-negative cell line .220.Immunity. 1998 Feb;8(2):221-31. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(00)80474-4. Immunity. 1998. PMID: 9492003
-
Accessory proteins that control the assembly of MHC molecules with peptides.Immunol Res. 2001;23(2-3):205-14. doi: 10.1385/IR:23:2-3:205. Immunol Res. 2001. PMID: 11444385 Review.
-
The role of tapasin in MHC class I antigen assembly.Immunol Res. 1999;20(2):79-88. doi: 10.1007/BF02786464. Immunol Res. 1999. PMID: 10580633 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of a tapasin mutant on the assembly of the mouse MHC class I molecule H2-K(d).Immunol Cell Biol. 2010 Jan;88(1):57-62. doi: 10.1038/icb.2009.59. Epub 2009 Aug 18. Immunol Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 19687800 Free PMC article.
-
Assembly of the MHC I peptide-loading complex determined by a conserved ionic lock-switch.Sci Rep. 2015 Nov 27;5:17341. doi: 10.1038/srep17341. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26611325 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of function of tapasin, a critical major histocompatibility complex class I assembly factor.Traffic. 2010 Mar;11(3):332-47. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2009.01025.x. Epub 2009 Dec 3. Traffic. 2010. PMID: 20070606 Free PMC article.
-
Newly discovered viral E3 ligase pK3 induces endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation of class I major histocompatibility proteins and their membrane-bound chaperones.J Biol Chem. 2012 Apr 27;287(18):14467-79. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.325340. Epub 2012 Mar 8. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22403403 Free PMC article.
-
Calreticulin in the immune system: ins and outs.Trends Immunol. 2013 Jan;34(1):13-21. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2012.08.002. Epub 2012 Sep 7. Trends Immunol. 2013. PMID: 22959412 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Allen H, Wraith D, Pala P, Askonas B, Flavell RA. Domain interactions of H-2 class I antigens alter cytotoxic T-cell recognition sites. Nature. 1984;309:279–281. - PubMed
-
- Bangia N, Lehner PJ, Hughes EA, Surman M, Cresswell P. The N-terminal region of tapasin is required to stabilize the MHC class I loading complex. Eur J Immunol. 1999;29:1858–1870. - PubMed
-
- Barnden MJ, Purcell AW, Gorman JJ, McCluskey J. Tapasin-mediated retention and optimization of peptide ligands during the assembly of class I molecules. J Immunol. 2000;165:322–330. - PubMed
-
- Carreno BM, Hansen TH. Exogenous peptide ligand influences the expression and half-life of free HLA class I heavy chains ubiquitously detected at the cell surface. Eur J Immunol. 1994;24:1285–1292. - PubMed
-
- Carreno B, Solheim JC, Harris M, Stroynowski I, Connolly JM, Hansen TH. TAP associates with a unique class I conformation, whereas calnexin associates with multiple class I forms in mouse and man. J Immunol. 1995;155:4726–4733. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

