Effect of latanoprost and timolol on the histopathology of the human conjunctiva
- PMID: 18971237
- PMCID: PMC2628534
- DOI: 10.1136/bjo.2008.140186
Effect of latanoprost and timolol on the histopathology of the human conjunctiva
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the effect of timolol and latanoprost on the extracellular matrix organisation, inflammatory infiltration, and expression of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and tissue inhibitors of matrix metalloproteinases (TIMPs) in the human conjunctiva.
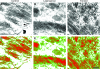
Methods: Conjunctival biopsies were obtained from the inferior fornix during routine cataract surgery from 20 patients with primary open-angle glaucoma, who had received a monotherapy either with timolol or latanoprost, and from 10 non-glaucomatous patients. Specimens were investigated by light microscopy, immunohistochemistry using antibodies against MMP-1,-3, TIMP-2,-3 and CD 68 antibodies and by quantitative transmission electron microscopy.
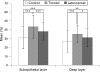
Results: The number of collagen fibres was significantly decreased in latanoprost-treated conjunctival specimens compared with timolol-treated eyes (p<0.01) but showed no difference to controls. Amorphous material was increased in both treated groups compared with controls (p<0.001) but was less in latanoprost-treated specimens compared with timolol-treated eyes (p<0.001). Optically clear spaces, probably containing glycosaminoglycans, were significantly reduced in both treated groups-with less of a reduction in latanoprost-compared with timolol-treated eyes (p<0.001). A marked upregulation of MMP-1 and MMP-3 and moderately increased staining for TIMP-2 and TIMP-3 was found in epithelial cells and subepithelial stromal cells of latanoprost-treated eyes. A moderate infiltration with macrophages and inflammatory cells was observed in timolol-treated eyes.
Conclusions: Latanoprost-treated conjunctival specimens showed a decreased stromal collagen density and a less pronounced inflammatory infiltration. The upregulation of MMP-1 and MMP-3 in latanoprost-treated eyes might explain the reduced extracellular matrix accumulation in the conjunctival stroma. Therefore, latanoprost therapy might have a more favourable effect on the outcome of glaucoma filtering surgery.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Broadway DC, Grierson I, O’Brien C, et al. Adverse effects of topical antiglaucoma medication. I. The conjunctival cell profile. Arch Ophthalmol 1994;112:1437–45 - PubMed
-
- Steuhl KP, Knorr M, Frohn A, et al. Effect of anti-glaucoma eye drops on cell differentiation of the conjunctiva. Fortschr Ophthalmol. 1991;88:865–9. German. - PubMed
-
- Schwab IR, Linberg JV, Gioia VM, et al. Foreshortening of the inferior conjunctival fornix associated with chronic glaucoma medications. Ophthalmology 1992;99:197–202 - PubMed
-
- Nuzzi R, Vercelli A, Finazzo C, et al. Conjunctiva and subconjunctival tissue in primary open-angle glaucoma after long-term topical treatment: an immunohistochemical and ultrastructural study. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 1995;233:154–62 - PubMed
-
- Baudouin C, Hamard P, Liang H, et al. Conjunctival epithelial cell expression of interleukins and inflammatory markers in glaucoma patients treated over the long term. Ophthalmology 2004;111:2186–92 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
