Homodimerization of Marek's disease virus-encoded Meq protein is not sufficient for transformation of lymphocytes in chickens
- PMID: 18971275
- PMCID: PMC2612399
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01630-08
Homodimerization of Marek's disease virus-encoded Meq protein is not sufficient for transformation of lymphocytes in chickens
Abstract
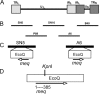
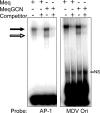
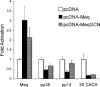
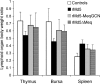
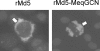
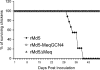
Marek's disease virus (MDV), the etiologic agent of Marek's disease, is a potent oncogenic herpesvirus. MDV is highly contagious and elicits a rapid onset of malignant T-cell lymphomas in chickens within several weeks after infection. MDV genome codes an oncoprotein, Meq, which shares resemblance with the Jun/Fos family of bZIP transcription factors. Similar to Jun, the leucine zipper region of Meq allows the formation of homo- and heterodimers. Meq homo- and heterodimers have different DNA binding affinities and transcriptional activity; therefore, they may differentially regulate transcription of viral and cellular genes. In this study we investigated the role of Meq homodimers in the pathogenicity of MDV by generating a chimeric meq gene, which contains the leucine zipper region of the yeast transcription factor GCN4 (meqGCN). A recombinant virus (rMd5-MeqGCN) containing the chimeric meqGCN gene in place of parental meq was generated with overlapping cosmid clones of Md5, a very virulent MDV strain. The rMd5-MeqGCN virus replicated in vitro and in vivo but was unable to transform T cells in infected chickens. These data provide the first in vivo evidence that Meq homodimers are not sufficient for MDV-induced transformation.
Figures

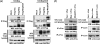

Similar articles
-
Selection of a recombinant Marek's disease virus in vivo through expression of the Marek's EcoRI-Q (Meq)-encoded oncoprotein: characterization of an rMd5-based mutant expressing the Meq of strain RB-1B.Avian Dis. 2012 Jun;56(2):328-40. doi: 10.1637/9955-100611-Reg.1. Avian Dis. 2012. PMID: 22856190
-
Marek's Disease Virus (MDV) Meq Oncoprotein Plays Distinct Roles in Tumor Incidence, Distribution, and Size.Viruses. 2025 Feb 14;17(2):259. doi: 10.3390/v17020259. Viruses. 2025. PMID: 40007015 Free PMC article.
-
Both homo and heterodimers of Marek's disease virus encoded Meq protein contribute to transformation of lymphocytes in chickens.Virology. 2010 Apr 10;399(2):312-21. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2010.01.006. Epub 2010 Feb 4. Virology. 2010. PMID: 20137800
-
Latency and tumorigenesis in Marek's disease.Avian Dis. 2013 Jun;57(2 Suppl):360-5. doi: 10.1637/10470-121712-Reg.1. Avian Dis. 2013. PMID: 23901747 Review.
-
Marek's disease virus reactivation from latency: changes in gene expression at the origin of replication.Poult Sci. 2003 Jun;82(6):893-8. doi: 10.1093/ps/82.6.893. Poult Sci. 2003. PMID: 12817443 Review.
Cited by
-
Methods for the Manipulation of Herpesvirus Genome and the Application to Marek's Disease Virus Research.Microorganisms. 2021 Jun 10;9(6):1260. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9061260. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 34200544 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Critical role of the virus-encoded microRNA-155 ortholog in the induction of Marek's disease lymphomas.PLoS Pathog. 2011 Feb;7(2):e1001305. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1001305. Epub 2011 Feb 24. PLoS Pathog. 2011. PMID: 21383974 Free PMC article.
-
Deletion of the Viral Thymidine Kinase in a Meq-Deleted Recombinant Marek's Disease Virus Reduces Lymphoid Atrophy but Is Less Protective.Microorganisms. 2021 Dec 22;10(1):7. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10010007. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 35056456 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Effective and Safe Vaccine for Prevention of Marek's Disease Caused by Infection with a Very Virulent Plus (vv+) Marek's Disease Virus.Vaccines (Basel). 2021 Feb 16;9(2):159. doi: 10.3390/vaccines9020159. Vaccines (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33669421 Free PMC article.
-
The oncogenic microRNA OncomiR-21 overexpressed during Marek's disease lymphomagenesis is transactivated by the viral oncoprotein Meq.J Virol. 2013 Jan;87(1):80-93. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02449-12. Epub 2012 Oct 10. J Virol. 2013. PMID: 23055556 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Calnek, B. W. 1986. Marek's disease: a model for herpesvirus oncology. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 12293-320. - PubMed
-
- Calnek, B. W. 2001. Pathogenesis of Marek's disease virus infection. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 25525-55. - PubMed
-
- Calnek, B. W., H. K. Adldinger, and D. E. Kahn. 1970. Feather follicle epithelium: a source of enveloped and infectious cell-free herpesvirus from Marek's disease. Avian Dis. 14219-233. - PubMed
-
- Calnek, B. W., R. W. Harris, C. Buscaglia, K. A. Schat, and B. Lucio. 1998. Relationship between the immunosuppressive potential and the pathotype of Marek's disease virus isolates. Avian Dis. 42124-132. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

