LPS activation is required for migratory activity and antigen presentation by tolerogenic dendritic cells
- PMID: 18971286
- PMCID: PMC2700018
- DOI: 10.1189/jlb.0608374
LPS activation is required for migratory activity and antigen presentation by tolerogenic dendritic cells
Abstract
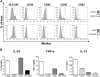
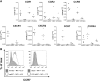
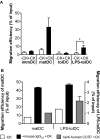
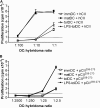
Autoimmune pathologies are caused by a breakdown in self-tolerance. Tolerogenic dendritic cells (tolDC) are a promising immunotherapeutic tool for restoring self-tolerance in an antigen-specific manner. Studies about tolDC have focused largely on generating stable maturation-resistant DC, but few have fully addressed questions about the antigen-presenting and migratory capacities of these cells, prerequisites for successful immunotherapy. Here, we investigated whether human tolDC, generated with dexamethasone and the active form of vitamin D3, maintained their tolerogenic function upon activation with LPS (LPS-tolDC), while acquiring the ability to present exogenous autoantigen and to migrate in response to the CCR7 ligand CCL19. LPS activation led to important changes in the tolDC phenotype and function. LPS-tolDC, but not tolDC, expressed the chemokine receptor CCR7 and migrated in response to CCL19. Furthermore, LPS-tolDC were superior to tolDC in their ability to present type II collagen, a candidate autoantigen in rheumatoid arthritis. tolDC and LPS-tolDC had low stimulatory capacity for allogeneic, naïve T cells and skewed T cell polarization toward an anti-inflammatory phenotype, although LPS-tolDC induced significantly higher levels of IL-10 production by T cells. Our finding that LPS activation is essential for inducing migratory and antigen-presenting activity in tolDC is important for optimizing their therapeutic potential.
Figures
References
-
- Lutz M B, Schuler G. Immature, semi-mature and fully mature dendritic cells: which signals induce tolerance or immunity? Trends Immunol. 2002;23:445–449. - PubMed
-
- Mahnke K, Schmitt E, Bonifaz L, Enk A H, Jonuleit H. Immature, but not inactive: the tolerogenic function of immature dendritic cells. Immunol Cell Biol. 2002;80:477–483. - PubMed
-
- Steinman R M, Hawiger D, Nussenzweig M C. Tolerogenic dendritic cells. Annu Rev Immunol. 2003;21:685–711. - PubMed
-
- Moser M. Dendritic cells in immunity and tolerance—do they display opposite functions? Immunity. 2003;19:5–8. - PubMed
-
- Gorczynski R M, Bransom J, Cattral M, Huang X, Lei J, Xiaorong L, Min W P, Wan Y, Gauldie J. Synergy in induction of increased renal allograft survival after portal vein infusion of dendritic cells transduced to express TGFβ and IL-10, along with administration of CHO cells expressing the regulatory molecule OX-2. Clin Immunol. 2000;95:182–189. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

