Arabidopsis CLP1-SIMILAR PROTEIN3, an ortholog of human polyadenylation factor CLP1, functions in gametophyte, embryo, and postembryonic development
- PMID: 18971429
- PMCID: PMC2593670
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.108.129817
Arabidopsis CLP1-SIMILAR PROTEIN3, an ortholog of human polyadenylation factor CLP1, functions in gametophyte, embryo, and postembryonic development
Abstract
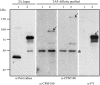
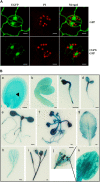
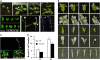
Polyadenylation factor CLP1 is essential for mRNA 3'-end processing in yeast and mammals. The Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) CLP1-SIMILAR PROTEIN3 (CLPS3) is an ortholog of human hCLP1. CLPS3 was previously found to be a subunit in the affinity-purified PCFS4-TAP (tandem affinity purification) complex involved in the alternative polyadenylation of FCA and flowering time control in Arabidopsis. In this article, we further explored the components in the affinity-purified CLPS3-TAP complex, from which Arabidopsis cleavage and polyadenylation specificity factor (CPSF) subunits AtCPSF100 and AtCPSF160 were found. This result implies that CLPS3 may bridge CPSF to the PCFS4 complex. Characterization of the CLPS3 mutant revealed that CLPS3 was essential for embryo development and important for female gametophyte transmission. Overexpression of CLPS3-TAP fusion caused a range of postembryonic development abnormalities, including early flowering time, altered phyllotaxy, and abnormal numbers and shapes of flower organs. These phenotypes are associated with the altered gene expression levels of FCA, WUS, and CUC1. The decreased ratio of FCA-beta to FCA-gamma in the overexpression plants suggests that CLPS3 favored the usage of FCA regular poly(A) site over the alternative site. These observations indicate that Arabidopsis CLPS3 might be involved in the processing of pre-mRNAs encoded by a distinct subset of genes that are important in plant development.
Figures



Comment in
-
Alternative polyadenylation: a mechanism maximizing transcriptome diversity in higher eukaryotes.Plant Signal Behav. 2009 May;4(5):440-2. doi: 10.1104/pp.108.129817. Epub 2009 May 6. Plant Signal Behav. 2009. PMID: 19816115 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alonso JM, Stepanova AN, Leisse TJ, Kim CJ, Chen H, Shinn P, Stevenson DK, Zimmerman J, Barajas P, Cheuk R, et al (2003) Genome-wide insertional mutagenesis of Arabidopsis thaliana. Science 301 653–657 - PubMed
-
- Brand U, Fletcher JC, Hobe M, Meyerowitz EM, Simon R, Fletcher JC, Brand U, Running MP, Simon R, Meyerowitz EM (2000) Dependence of stem cell fate in Arabidopsis on a feedback loop regulated by CLV3 activity. Science 289 617–619 - PubMed
-
- Castellano MM, Sablowski R (2005) Intercellular signalling in the transition from stem cells to organogenesis in meristems. Curr Opin Plant Biol 8 26–31 - PubMed
-
- Clough SJ, Bent AF (1998) Floral dip: a simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 16 735–743 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

