Effective motion-sensitizing magnetization preparation for black blood magnetic resonance imaging of the heart
- PMID: 18972350
- PMCID: PMC2666444
- DOI: 10.1002/jmri.21568
Effective motion-sensitizing magnetization preparation for black blood magnetic resonance imaging of the heart
Abstract
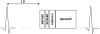
Purpose: To investigate the effectiveness of flow signal suppression of a motion-sensitizing magnetization preparation (MSPREP) sequence and to optimize a 2D MSPREP steady-state free precession (SSFP) sequence for black blood imaging of the heart.
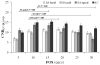
Materials and methods: Using a flow phantom, the effect of varying field of speed (FOS), b-value, voxel size, and flow pattern on the flow suppression was investigated. In seven healthy volunteers, black blood images of the heart were obtained at 1.5T with MSPREP-SSFP and double inversion recovery fast spin echo (DIR-FSE) techniques. Myocardium and blood signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and myocardium-to-blood contrast-to-noise ratio (CNR) were measured. The optimal FOS that maximized the CNR for MSPREP-SSFP was determined.
Results: Phantom data demonstrated that the flow suppression was induced primarily by the velocity encoding effect. In humans, FOS=10-20 cm/s was found to maximize the CNR for short-axis (SA) and four-chamber (4C) views. Compared to DIR-FSE, MSPREP-SSFP provided similar blood SNR efficiency in the SA basal and mid-views and significantly lower blood SNR efficiency in the SA apical (P=0.02) and 4C (P=0.01) views, indicating similar or better blood suppression.
Conclusion: Velocity encoding is the primary flow suppression mechanism of the MSPREP sequence and 2D MSPREP-SSFP black blood imaging of the heart is feasible in healthy subjects.
Copyright (c) 2008 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures

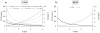




References
-
- Edelman RR, Chien D, Kim D. Fast selective black blood MR imaging. Radiology. 1991;181:655–660. - PubMed
-
- Simonetti OP, Finn JP, White RD, Laub G, Henry DA. “Black blood” T2-weighted inversion-recovery MR imaging of the heart. Radiology. 1996;199:49–57. - PubMed
-
- Parker DL, Goodrich KC, Masiker M, Tsuruda JS, Katzman GL. Improved efficiency in double-inversion fast spin-echo imaging. Magn Reson Med. 2002;47:1017–1021. - PubMed
-
- Song HK, Wright AC, Wolf RL, Wehrli FW. Multislice double inversion pulse sequence for efficient black-blood MRI. Magn Reson Med. 2002;47:616–620. - PubMed
-
- Yarnykh VL, Yuan C. Multislice double inversion-recovery black-blood imaging with simultaneous slice reinversion. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2003;17:478–483. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

