The effect of high dose melatonin on cardiac ischemia- reperfusion Injury
- PMID: 18972593
- PMCID: PMC2615373
- DOI: 10.3349/ymj.2008.49.5.735
The effect of high dose melatonin on cardiac ischemia- reperfusion Injury
Abstract
Purpose: Melatonin, the most potent scavenger of toxic free radicals, has been found to be effective in protecting against pathological states due to the release of reactive oxygen species. This study was performed to establish the effect of high dose melatonin on protection against ischemia- reperfusion (I/R) injury in rat hearts.
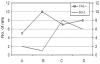
Materials and methods: Forty male Sprague-Dawley rats were used in this study. They were separated into four groups of ten rats each. A left coronary artery occlusion was induced in the rats by ligating the artery for 20 minutes and then releasing the ligation (reperfusion) afterwards. The control group was Group A. Group B was subjected to myocardial ischemia-reperfusion without any treatment, while Group C underwent myocardial ischemia-reperfusion with a melatonin treatment before the ischemia. Group D was subjected to myocardial ischemia-reperfusion with a melatonin treatment before the reperfusion. After 20 minutes of reperfusion, blood samples were obtained from each group for biochemical studies, and the animals were sacrificed for histological and, immunohistochemical examinations of the myocardial tissue.
Results: We found that the cardiac troponin T(cTn-T) levels were significantly increased in Group B when all groups were compared. In the Group C rats treated with melatonin, the cTn-T values were significantly lower than those in Groups B and D. In addition, malondialdehyde (MDA) and antioxidant enzymes including, superoxide dismutase (SOD) and myeloperoxidase (MPO) were lower than those in Group B in the melatonin treated groups. The differences were statistically significant (p < 0.05). Histopathologic and immunohistopathologic studies also supported the effectiveness of melatonin.
Conclusion: Our study suggests that high dose melatonin, appears to offer protection against cardiac ischemia-reperfusion injuries in rats by scavenging the free radicals and could have a potential clinical use in the management of myocardial ischemia.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The protective effect of melatonin on nicotine-induced myocardial injury in newborn rats whose mothers received nicotine.Anadolu Kardiyol Derg. 2008 Aug;8(4):243-8. Anadolu Kardiyol Derg. 2008. PMID: 18676298
-
Beneficial effect of raxofelast, an hydrophilic vitamin E analogue, in the rat heart after ischemia and reperfusion injury.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1998 Aug;30(8):1493-503. doi: 10.1006/jmcc.1998.0713. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1998. PMID: 9737936
-
The role of melatonin in prevention of intestinal ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats.J Pediatr Surg. 2000 Oct;35(10):1444-8. doi: 10.1053/jpsu.2000.16410. J Pediatr Surg. 2000. PMID: 11051147
-
[Myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury and melatonin].Anadolu Kardiyol Derg. 2006 Jun;6(2):163-8. Anadolu Kardiyol Derg. 2006. PMID: 16766282 Review. Turkish.
-
Oxidative and inflammatory biomarkers of ischemia and reperfusion injuries.Dan Med J. 2015 Apr;62(4):B5054. Dan Med J. 2015. PMID: 25872540 Review.
Cited by
-
Melatonin as a therapy in cardiac ischemia-reperfusion injury: Potential mechanisms by which MT2 activation mediates cardioprotection.J Adv Res. 2020 Sep 28;29:33-44. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2020.09.007. eCollection 2021 Mar. J Adv Res. 2020. PMID: 33842003 Free PMC article.
-
Myosin 1b Participated in the Modulation of Hypoxia/Reoxygenation-Caused H9c2 Cell Apoptosis and Autophagy.Anal Cell Pathol (Amst). 2022 Nov 22;2022:5187304. doi: 10.1155/2022/5187304. eCollection 2022. Anal Cell Pathol (Amst). 2022. PMID: 36458211 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of melatonin and its receptors in cardiac ischemia-reperfusion injury.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2018 Nov;75(22):4125-4149. doi: 10.1007/s00018-018-2905-x. Epub 2018 Aug 13. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2018. PMID: 30105616 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Radiation protection following nuclear power accidents: a survey of putative mechanisms involved in the radioprotective actions of taurine during and after radiation exposure.Microb Ecol Health Dis. 2012 Feb 1;23. doi: 10.3402/mehd.v23i0.14787. eCollection 2012. Microb Ecol Health Dis. 2012. PMID: 23990836 Free PMC article.
-
Preparation and activity analysis of recombinant human high-density lipoprotein.Assay Drug Dev Technol. 2012 Oct;10(5):485-91. doi: 10.1089/adt.2012.467. Epub 2012 Aug 16. Assay Drug Dev Technol. 2012. PMID: 22897450 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hearse DJ, Bolli R. Reperfusion induced injury: manifestations, mechanisms, and clinical relevance. Cardiovasc Res. 1992;26:101–108. - PubMed
-
- Yue TL, Ma XL, Wang X, Romanic AM, Liu GL, Louden C, et al. Possible involvement of stress-activated protein kinase signaling pathway and Fas receptor expression in prevention of ischemia/reperfusion-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis by carvedilol. Circ Res. 1998;82:166–174. - PubMed
-
- Kaneko S, Okumura K, Numaguchi Y, Matsui H, Murase K, Mokuno S, et al. Melatonin scavenges hydroxyl radical and protects isolated rat hearts from ischemic reperfusion injury. Life Sci. 2000;67:101–112. - PubMed
-
- Tan DX, Chen LD, Poeggeler B, Manchester LC, Reiter RJ. Melatonin: a potent, endogenous hydroxyl radical scavenger. Endocr J. 1993;1:57–60.
-
- Reiter RJ, Poeggeler B, Tan DX, Chen LD, Manchester LC, Cuerrero JM. Antioxidant capacity of melatonin: a novel action not requiring receptor. Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 1993;15:103–116.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

