IMP dehydrogenase type 1 associates with polyribosomes translating rhodopsin mRNA
- PMID: 18974094
- PMCID: PMC2605994
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M806143200
IMP dehydrogenase type 1 associates with polyribosomes translating rhodopsin mRNA
Abstract
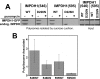
IMP dehydrogenase (IMPDH) catalyzes the pivotal step in guanine nucleotide biosynthesis. Here we show that both IMPDH type 1 (IMPDH1) and IMPDH type 2 are associated with polyribosomes, suggesting that these housekeeping proteins have an unanticipated role in translation regulation. This interaction is mediated by the subdomain, a region of disputed function that is the site of mutations that cause retinal degeneration. The retinal isoforms of IMPDH1 also associate with polyribosomes. The most common disease-causing mutation, D226N, disrupts the polyribosome association of at least one retinal IMPDH1 isoform. Finally, we find that IMPDH1 is associated with polyribosomes containing rhodopsin mRNA. Because any perturbation of rhodopsin expression can trigger apoptosis in photoreceptor cells, these observations suggest a likely pathological mechanism for IMPDH1-mediated hereditary blindness. We propose that IMPDH coordinates the translation of a set of mRNAs, perhaps by modulating localization or degradation.
Figures





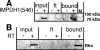
References
-
- Weber, G., Nakamura, H., Natsumeda, Y., Szekeres, T., and Nagai, M. (1992) Adv. Enzyme Regul. 32 57-69 - PubMed
-
- Nimmesgern, E., Black, J., Futer, O., Fulghum, J. R., Chambers, S. P., Brummel, C. L., Raybuck, S. A., and Sintchak, M. D. (1999) Protein Expression Purif. 17 282-289 - PubMed
-
- Gan, L., Petsko, G. A., and Hedstrom, L. (2002) Biochemistry 41 13309-13317 - PubMed
-
- Janosik, M., Kery, V., Gaustadnes, M., Maclean, K. N., and Kraus, J. P. (2001) Biochemistry 40 10625-10633 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

