c-Cbl interacts with CD38 and promotes retinoic acid-induced differentiation and G0 arrest of human myeloblastic leukemia cells
- PMID: 18974118
- PMCID: PMC4896297
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-1058
c-Cbl interacts with CD38 and promotes retinoic acid-induced differentiation and G0 arrest of human myeloblastic leukemia cells
Abstract
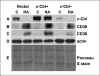
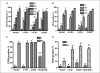
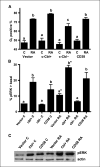
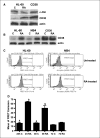
Retinoic acid (RA) is known to regulate cell growth and differentiation. In HL-60 human myeloblastic leukemia cells, it causes mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling leading to myeloid differentiation and G(0) cell cycle arrest. This communication reports that expression of the Cbl adaptor caused enhanced extracellular signal-regulated kinase 2 activation and promoted RA-induced differentiation and G(0)-arrest. Stable transfectants ectopically expressing c-Cbl underwent myeloid differentiation faster than wild-type (wt) cells when treated with RA. In contrast, c-Cbl knockdown stable transfectants differentiated slower than wt cells when treated with RA. Cells ectopically expressing c-Cbl had enhanced CD38 expression when treated with RA, and cells ectopically expressing CD38 had enhanced c-Cbl expression, even without with RA, suggesting an interaction between c-Cbl and CD38. Fluorescence resource energy transfer and coimmunoprecipitation showed that c-Cbl and CD38 bind each other. RA causes the gradual down-regulation and eventual loss of c-Cbl expression, resulting in loss of the Cbl-CD38 interaction, suggesting that c-Cbl plays a relatively early role in promoting RA-induced differentiation. RA-induced differentiation can thus be propelled by c-Cbl and by CD38, both of which bind together, enhance the expression of each other, and cause MAPK signaling. There thus seems to be a cooperative role for c-Cbl and CD38, reflected in their direct binding, in propulsion of RA-induced differentiation.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Interferon regulatory factor-1 binds c-Cbl, enhances mitogen activated protein kinase signaling and promotes retinoic acid-induced differentiation of HL-60 human myelo-monoblastic leukemia cells.Leuk Lymphoma. 2011 Dec;52(12):2372-9. doi: 10.3109/10428194.2011.603449. Epub 2011 Aug 24. Leuk Lymphoma. 2011. PMID: 21740303 Free PMC article.
-
6-Formylindolo(3,2-b)Carbazole (FICZ) Modulates the Signalsome Responsible for RA-Induced Differentiation of HL-60 Myeloblastic Leukemia Cells.PLoS One. 2015 Aug 19;10(8):e0135668. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0135668. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26287494 Free PMC article.
-
c-Cbl tyrosine kinase-binding domain mutant G306E abolishes the interaction of c-Cbl with CD38 and fails to promote retinoic acid-induced cell differentiation and G0 arrest.J Biol Chem. 2009 Sep 18;284(38):25664-77. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.014241. Epub 2009 Jul 27. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19635790 Free PMC article.
-
Retinoic acid induces expression of SLP-76: expression with c-FMS enhances ERK activation and retinoic acid-induced differentiation/G0 arrest of HL-60 cells.Eur J Cell Biol. 2006 Feb;85(2):117-32. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2005.09.020. Epub 2005 Nov 11. Eur J Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16439309
-
Retinoic acid induced mitogen-activated protein (MAP)/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) kinase-dependent MAP kinase activation needed to elicit HL-60 cell differentiation and growth arrest.Cancer Res. 1998 Jul 15;58(14):3163-72. Cancer Res. 1998. PMID: 9679985
Cited by
-
Interferon regulatory factor-1 binds c-Cbl, enhances mitogen activated protein kinase signaling and promotes retinoic acid-induced differentiation of HL-60 human myelo-monoblastic leukemia cells.Leuk Lymphoma. 2011 Dec;52(12):2372-9. doi: 10.3109/10428194.2011.603449. Epub 2011 Aug 24. Leuk Lymphoma. 2011. PMID: 21740303 Free PMC article.
-
ATRA-induced HL-60 myeloid leukemia cell differentiation depends on the CD38 cytosolic tail needed for membrane localization, but CD38 enzymatic activity is unnecessary.Exp Cell Res. 2011 Apr 15;317(7):910-9. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2010.12.003. Epub 2010 Dec 13. Exp Cell Res. 2011. PMID: 21156171 Free PMC article.
-
6-Formylindolo(3,2-b)Carbazole (FICZ) Modulates the Signalsome Responsible for RA-Induced Differentiation of HL-60 Myeloblastic Leukemia Cells.PLoS One. 2015 Aug 19;10(8):e0135668. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0135668. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26287494 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear Raf-1 kinase regulates the CXCR5 promoter by associating with NFATc3 to drive retinoic acid-induced leukemic cell differentiation.FEBS J. 2014 Feb;281(4):1170-80. doi: 10.1111/febs.12693. Epub 2014 Jan 10. FEBS J. 2014. PMID: 24330068 Free PMC article.
-
Retinoic acid induces nuclear accumulation of Raf1 during differentiation of HL-60 cells.Exp Cell Res. 2009 Aug 1;315(13):2241-8. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2009.03.004. Epub 2009 Mar 17. Exp Cell Res. 2009. PMID: 19298812 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sklan D. Vitamin A in human nutrition. Prog Food Nut Sci. 1987;11:39–55. - PubMed
-
- Mann G, Reinhardt D, Ritter J, et al. Treatment with all-trans retinoic acid in acute promyelocytic leukemia reduces early death in children. Ann Hematol. 2001;80:417–22. - PubMed
-
- Collins SJ, Gallo RC, Gallagher RE. Continuous growth and differentiation of human myeloid leukaemic cells in suspension culture. Nature. 1977;270:347–9. - PubMed
-
- Yen A. HL-60 cells as a model of growth control and differentiation: the significance of variant cells. Hematol Rev. 1990;4:5–46.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

