Adipose inflammation, insulin resistance, and cardiovascular disease
- PMID: 18974244
- PMCID: PMC3088110
- DOI: 10.1177/0148607108325251
Adipose inflammation, insulin resistance, and cardiovascular disease
Abstract
Adiposity-associated inflammation and insulin resistance are strongly implicated in the development of type 2 diabetes and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. This article reviews the mechanisms of adipose inflammation, because these may represent therapeutic targets for insulin resistance and for prevention of metabolic and cardiovascular consequences of obesity. The initial insult in adipose inflammation and insulin resistance, mediated by macrophage recruitment and endogenous ligand activation of Toll-like receptors, is perpetuated through chemokine secretion, adipose retention of macrophages, and elaboration of pro-inflammatory adipocytokines. Activation of various kinases modulates adipocyte transcription factors, including peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma and NFkappaB, attenuating insulin signaling and increasing adipocytokine and free fatty acid secretion. Inflammation retards adipocyte differentiation and further exacerbates adipose dysfunction and inflammation. Paracrine and endocrine adipose inflammatory events induce a local and systemic inflammatory, insulin-resistant state promoting meta-bolic dyslipidemia, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular disease. Developing therapeutic strategies that target both adipose inflammation and insulin resistance may help to prevent type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease in the emerging epidemic of obesity.
Figures
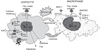
References
-
- Goodpaster BH, Krishnaswami S, Harris TB, et al. Obesity, regional body fat distribution, and the metabolic syndrome in older men and women. Arch Intern Med. 2005;165:777–783. - PubMed
-
- Zeyda M, Farmer D, Todoric J, et al. Human adipose tissue macrophages are of an anti-inflammatory phenotype but capable of excessive pro-inflammatory mediator production. Int J Obes (Lond) 2007;31:1420–1428. - PubMed
-
- Permana PA, Menge C, Reaven PD. Macrophage-secreted factors induce adipocyte inflammation and insulin resistance. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006;341:507–514. - PubMed
-
- Cani PD, Amar J, Iglesias MA, et al. Metabolic endotoxemia initiates obesity and insulin resistance. Diabetes. 2007;56:1761–1772. - PubMed
-
- Tilg H, Moschen AR. Adipocytokines: mediators linking adipose tissue, inflammation and immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 2006;6:772–783. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

