Aneuploidy affects proliferation and spontaneous immortalization in mammalian cells
- PMID: 18974345
- PMCID: PMC2701511
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1160058
Aneuploidy affects proliferation and spontaneous immortalization in mammalian cells
Abstract
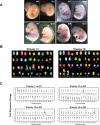
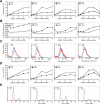
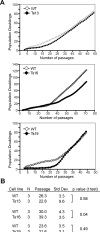
Aneuploidy, an incorrect number of chromosomes, is the leading cause of miscarriages and mental retardation in humans and is a hallmark of cancer. We examined the effects of aneuploidy on primary mouse cells by generating a series of cell lines that carry an extra copy of one of four mouse chromosomes. In all four trisomic lines, proliferation was impaired and metabolic properties were altered. Immortalization, the acquisition of the ability to proliferate indefinitely, was also affected by the presence of an additional copy of certain chromosomes. Our data indicate that aneuploidy decreases not only organismal but also cellular fitness and elicits traits that are shared between different aneuploid cells.
Figures

Comment in
-
Cancer. Aneuploidy advantages?Science. 2008 Oct 31;322(5902):692-3. doi: 10.1126/science.1166151. Science. 2008. PMID: 18974340 No abstract available.
-
The aneuploidy paradox in cell growth and tumorigenesis.Cancer Cell. 2008 Dec 9;14(6):431-3. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2008.11.011. Cancer Cell. 2008. PMID: 19061834 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

