Polycomb proteins targeted by a short repeat RNA to the mouse X chromosome
- PMID: 18974356
- PMCID: PMC2748911
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1163045
Polycomb proteins targeted by a short repeat RNA to the mouse X chromosome
Abstract
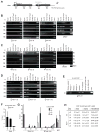
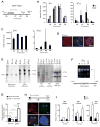
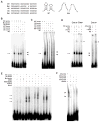
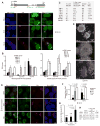
To equalize X-chromosome dosages between the sexes, the female mammal inactivates one of her two X chromosomes. X-chromosome inactivation (XCI) is initiated by expression of Xist, a 17-kb noncoding RNA (ncRNA) that accumulates on the X in cis. Because interacting factors have not been isolated, the mechanism by which Xist induces silencing remains unknown. We discovered a 1.6-kilobase ncRNA (RepA) within Xist and identified the Polycomb complex, PRC2, as its direct target. PRC2 is initially recruited to the X by RepA RNA, with Ezh2 serving as the RNA binding subunit. The antisense Tsix RNA inhibits this interaction. RepA depletion abolishes full-length Xist induction and trimethylation on lysine 27 of histone H3 of the X. Likewise, PRC2 deficiency compromises Xist up-regulation. Therefore, RepA, together with PRC2, is required for the initiation and spread of XCI. We conclude that a ncRNA cofactor recruits Polycomb complexes to their target locus.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

