Cellular procoagulant activity dictates clot structure and stability as a function of distance from the cell surface
- PMID: 18974382
- PMCID: PMC2773697
- DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.108.176008
Cellular procoagulant activity dictates clot structure and stability as a function of distance from the cell surface
Abstract
Background: Thrombin concentration modulates fibrin structure and fibrin structure modulates clot stability; however, the impact of localized, cell surface-driven in situ thrombin generation on fibrin structure and stability has not previously been evaluated.
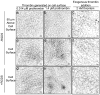
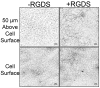
Methods and results: Human fibroblasts were incubated with factors Xa, Va, prothrombin and fibrinogen, or plasma. Fibrin formation, structure, and lysis were examined using laser scanning confocal microscopy and transmission electron microscopy. In situ thrombin generation on the cell surface produced clots with a significantly denser fiber network in a 10-microm region proximal versus distal to (40 to 50 microm) the cell surface. This morphology was not altered by addition of integrin-blocking RGDS peptide and was not apparent in clots made by exogenous thrombin addition, suggesting that spatial morphology was dictated predominantly by localized thrombin generation on the fibroblast surface. The fibrin network lysed more rapidly distal versus proximal to the cell surface, suggesting that the structural heterogeneity of the clot affected its fibrinolytic stability.
Conclusions: In situ thrombin generation on the cell surface modulates the three-dimensional structure and stability of the clot. Thrombus formation in vivo may reflect the ability of the local cell population to support thrombin generation and, therefore, the three-dimensional structure and stability of the fibrin network.
Figures









Similar articles
-
Contributions of extravascular and intravascular cells to fibrin network formation, structure, and stability.Blood. 2009 Nov 26;114(23):4886-96. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-06-228940. Epub 2009 Oct 1. Blood. 2009. PMID: 19797520 Free PMC article.
-
Factor XIIa regulates the structure of the fibrin clot independently of thrombin generation through direct interaction with fibrin.Blood. 2011 Oct 6;118(14):3942-51. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-03-339572. Epub 2011 Aug 9. Blood. 2011. PMID: 21828145
-
Cardiac Myosin Promotes Thrombin Generation and Coagulation In Vitro and In Vivo.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2020 Apr;40(4):901-913. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.120.313990. Epub 2020 Feb 27. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2020. PMID: 32102568 Free PMC article.
-
Thrombin generation and fibrin clot structure.Blood Rev. 2007 May;21(3):131-42. doi: 10.1016/j.blre.2006.11.001. Epub 2007 Jan 8. Blood Rev. 2007. PMID: 17208341 Review.
-
Thrombin generation, fibrin clot formation and hemostasis.Transfus Apher Sci. 2008 Feb;38(1):15-23. doi: 10.1016/j.transci.2007.12.005. Epub 2008 Feb 20. Transfus Apher Sci. 2008. PMID: 18282807 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Hydrogel-Assisted Antisense LNA Gapmer Delivery for In Situ Gene Silencing in Spinal Cord Injury.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2018 Jun 1;11:393-406. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2018.03.009. Epub 2018 Mar 20. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2018. PMID: 29858074 Free PMC article.
-
Toward an understanding of fibrin branching structure.Phys Rev E Stat Nonlin Soft Matter Phys. 2010 May;81(5 Pt 1):051922. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.81.051922. Epub 2010 May 24. Phys Rev E Stat Nonlin Soft Matter Phys. 2010. PMID: 20866276 Free PMC article.
-
Association between biomarkers of endothelial injury and hypocoagulability in patients with severe sepsis: a prospective study.Crit Care. 2015 Apr 24;19(1):191. doi: 10.1186/s13054-015-0918-5. Crit Care. 2015. PMID: 25907781 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Fibrinogen and Fibrin in Hemostasis and Thrombosis.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2017 Mar;37(3):e13-e21. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.117.308564. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2017. PMID: 28228446 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Role, Laboratory Assessment and Clinical Relevance of Fibrin, Factor XIII and Endogenous Fibrinolysis in Arterial and Venous Thrombosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 2;22(3):1472. doi: 10.3390/ijms22031472. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33540604 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Collet JP, Allali Y, Lesty C, Tanguy ML, Silvain J, Ankri A, Blanchet B, Dumaine R, Gianetti J, Payot L, Weisel JW, Montalescot G. Altered fibrin architecture is associated with hypofibrinolysis and premature coronary atherothrombosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2006;26:2567–2573. - PubMed
-
- Fatah K, Hamsten A, Blomback B, Blomback M. Fibrin gel network characteristics and coronary heart disease: relations to plasma fibrinogen concentration, acute phase protein, serum lipoproteins and coronary atherosclerosis. Thromb Haemost. 1992;68:130–135. - PubMed
-
- Fatah K, Silveira A, Tornvall P, Karpe F, Blomback M, Hamsten A. Proneness to formation of tight and rigid fibrin gel structures in men with myocardial infarction at a young age. Thromb Haemost. 1996;76:535–540. - PubMed
-
- Bounameaux H. Factor V Leiden paradox: risk of deep-vein thrombosis but not of pulmonary embolism. Lancet. 2000;356:182–183. - PubMed
-
- Blomback B, Carlsson K, Hessel B, Liljeborg A, Procyk R, Aslund N. Native fibrin gel networks observed by 3D microscopy, permeation and turbidity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989;997:96–110. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

