Deficiency of FLCN in mouse kidney led to development of polycystic kidneys and renal neoplasia
- PMID: 18974783
- PMCID: PMC2570491
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0003581
Deficiency of FLCN in mouse kidney led to development of polycystic kidneys and renal neoplasia
Erratum in
- PLoS ONE. 2008;3(11). doi: 10.1371/annotation/0f06471c-1993-4144-b785-d58924ac0b5c doi: 10.1371/annotation/0f06471c-1993-4144-b785-d58924ac0b5c
- PLoS ONE. 2008;3(11). doi: 10.1371/annotation/136385d5-b241-4ecc-b31a-6dea3ebf3bc4. Dykyma, Karl [corrected to Dykema, Karl] doi: 10.1371/annotation/136385d5-b241-4ecc-b31a-6dea3ebf3bc4
Abstract
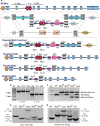
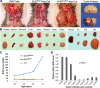
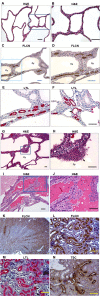
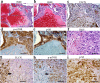
The Birt-Hogg-Dubé (BHD) disease is a genetic cancer syndrome. The responsible gene, BHD, has been identified by positional cloning and thought to be a novel tumor suppressor gene. BHD mutations cause many types of diseases including renal cell carcinomas, fibrofolliculomas, spontaneous pneumothorax, lung cysts, and colonic polyps/cancers. By combining Gateway Technology with the Ksp-Cre gene knockout system, we have developed a kidney-specific BHD knockout mouse model. BHD(flox/flox)/Ksp-Cre mice developed enlarged kidneys characterized by polycystic kidneys, hyperplasia, and cystic renal cell carcinoma. The affected BHD(flox/flox)/Ksp-Cre mice died of renal failure at approximate three weeks of age, having blood urea nitrogen levels over tenfold higher than those of BHD (flox/+)/Ksp-Cre and wild-type littermate controls. We further demonstrated that these phenotypes were caused by inactivation of BHD and subsequent activation of the mTOR pathway. Application of rapamycin, which inhibits mTOR activity, to the affected mice led to extended survival and inhibited further progression of cystogenesis. These results provide a correlation of kidney-targeted gene inactivation with renal carcinoma, and they suggest that the BHD product FLCN, functioning as a cyst and tumor suppressor, like other hamartoma syndrome-related proteins such as PTEN, LKB1, and TSC1/2, is a component of the mTOR pathway, constituting a novel FLCN-mTOR signaling branch that regulates cell growth/proliferation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Birt AR, Hogg GR, Dube WJ. Hereditary multiple fibrofolliculomas with trichodiscomas and acrochordons. Arch Dermatol. 1977;113:1674–1677. - PubMed
-
- Welsch MJ, Krunic A, Medenica MM. Birt-Hogg-Dube Syndrome. Int J Dermatol. 2005;44:668–673. - PubMed
-
- Lindor NM, Hand J, Burch PA, Gibson LE. Birt-Hogg-Dube syndrome: an autosomal dominant disorder with predisposition to cancers of the kidney, fibrofolliculomas, and focal cutaneous mucinosis. Int J Dermatol. 2001;40:653–656. - PubMed
-
- Khoo SK, Bradley M, Wong FK, Hedblad MA, Nordenskjold M, et al. Birt-Hogg-Dube syndrome: mapping of a novel hereditary neoplasia gene to chromosome 17p12–q11.2. Oncogene. 2001;20:5239–5242. - PubMed
-
- Nickerson ML, Warren MB, Toro JR, Matrosova V, Glenn G, et al. Mutations in a novel gene lead to kidney tumors, lung wall defects, and benign tumors of the hair follicle in patients with the Birt-Hogg-Dube syndrome. Cancer Cell. 2002;2:157–164. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

