The Neuroterrain 3D Mouse Brain Atlas
- PMID: 18974795
- PMCID: PMC2525976
- DOI: 10.3389/neuro.11.003.2008
The Neuroterrain 3D Mouse Brain Atlas
Abstract
A significant objective of neuroinformatics is the construction of tools to readily access, search, and analyze anatomical imagery. This goal can be subdivided into development of the necessary databases and of the computer vision tools for image analysis. When considering mesoscale images, the latter tools can be further divided into registration algorithms and anatomical models. The models are atlases that contain both bitmap images and templates of anatomical boundaries. We report here on construction of such a model for the C57BL/6J mouse. The intended purpose of this atlas is to aid in automated delineation of the Mouse Brain Library, a database of brain histological images of importance to neurogenetic research.
Keywords: 3D reconstruction; atlas; automated segmentation; brain model; neuroanatomy; registration; spatial normalization; standard coordinate space.
Figures

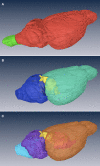
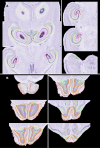
Similar articles
-
Constructing and optimizing 3D atlases from 2D data with application to the developing mouse brain.Elife. 2021 Feb 11;10:e61408. doi: 10.7554/eLife.61408. Elife. 2021. PMID: 33570495 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroinformatics of the Allen Mouse Brain Connectivity Atlas.Methods. 2015 Feb;73:4-17. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2014.12.013. Epub 2014 Dec 20. Methods. 2015. PMID: 25536338 Review.
-
Multi-atlas segmentation of the whole hippocampus and subfields using multiple automatically generated templates.Neuroimage. 2014 Nov 1;101:494-512. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2014.04.054. Epub 2014 Apr 29. Neuroimage. 2014. PMID: 24784800
-
NeuroTerrain--a client-server system for browsing 3D biomedical image data sets.BMC Bioinformatics. 2007 Feb 5;8:40. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-8-40. BMC Bioinformatics. 2007. PMID: 17280615 Free PMC article.
-
Brain templates and atlases.Neuroimage. 2012 Aug 15;62(2):911-22. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.01.024. Epub 2012 Jan 10. Neuroimage. 2012. PMID: 22248580 Review.
Cited by
-
MBAT: a scalable informatics system for unifying digital atlasing workflows.BMC Bioinformatics. 2010 Dec 22;11:608. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-11-608. BMC Bioinformatics. 2010. PMID: 21176225 Free PMC article.
-
Visualization of image data from cells to organisms.Nat Methods. 2010 Mar;7(3 Suppl):S26-41. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1431. Nat Methods. 2010. PMID: 20195255 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A deformable atlas of the laboratory mouse.Mol Imaging Biol. 2015 Feb;17(1):18-28. doi: 10.1007/s11307-014-0767-7. Mol Imaging Biol. 2015. PMID: 25049072 Free PMC article.
-
Digital atlasing and standardization in the mouse brain.PLoS Comput Biol. 2011 Feb 3;7(2):e1001065. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1001065. PLoS Comput Biol. 2011. PMID: 21304938 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Common atlas format and 3D brain atlas reconstructor: infrastructure for constructing 3D brain atlases.Neuroinformatics. 2012 Apr;10(2):181-97. doi: 10.1007/s12021-011-9138-6. Neuroinformatics. 2012. PMID: 22227717 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ardekani S. (2000). Inter-Animal Rodent Brain Alignment and Supervised 3D Reconstruction. Philadelphia, School of Biomedical Engineering, Science, and Health Systems, Drexel University, 92 p.
-
- Baldock R. A., Bard J. B. L., Burger A., Burton N., Christiansen J., Feng G., Hill B., Houghton D., Kaufman M., Rao J., Sharpe J., Ross A., Stevenson P., Venkataraman S., Waterhouse A., Yang Y., Davidson D. R. (2003). EMAP and EMAGE: a framework for understanding spatially organized data. Neuroinformatics 1, 309–32610.1385/NI:1:4:309 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Boline J., Bug W., Zaslavsky I., Williams R., Martone M., Anderson S., Wong W., Yuan H., Memon A., Ng Q., Grethe J., Sforza D., MacKenzie-Graham A., Nissanov J., Gustafson C., Toga A. (2007). Accessing a sharing infrastructure with the Mouse BIRN atlasing toolkit (MBAT). In Proceedings of the Society for Neuroscience 37th Annual Meeting, San Diego, CA, USA
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

