The Neuroterrain 3D Mouse Brain Atlas
- PMID: 18974795
- PMCID: PMC2525976
- DOI: 10.3389/neuro.11.003.2008
The Neuroterrain 3D Mouse Brain Atlas
Abstract
A significant objective of neuroinformatics is the construction of tools to readily access, search, and analyze anatomical imagery. This goal can be subdivided into development of the necessary databases and of the computer vision tools for image analysis. When considering mesoscale images, the latter tools can be further divided into registration algorithms and anatomical models. The models are atlases that contain both bitmap images and templates of anatomical boundaries. We report here on construction of such a model for the C57BL/6J mouse. The intended purpose of this atlas is to aid in automated delineation of the Mouse Brain Library, a database of brain histological images of importance to neurogenetic research.
Keywords: 3D reconstruction; atlas; automated segmentation; brain model; neuroanatomy; registration; spatial normalization; standard coordinate space.
Figures

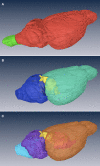
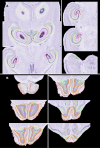
References
-
- Ardekani S. (2000). Inter-Animal Rodent Brain Alignment and Supervised 3D Reconstruction. Philadelphia, School of Biomedical Engineering, Science, and Health Systems, Drexel University, 92 p.
-
- Baldock R. A., Bard J. B. L., Burger A., Burton N., Christiansen J., Feng G., Hill B., Houghton D., Kaufman M., Rao J., Sharpe J., Ross A., Stevenson P., Venkataraman S., Waterhouse A., Yang Y., Davidson D. R. (2003). EMAP and EMAGE: a framework for understanding spatially organized data. Neuroinformatics 1, 309–32610.1385/NI:1:4:309 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Boline J., Bug W., Zaslavsky I., Williams R., Martone M., Anderson S., Wong W., Yuan H., Memon A., Ng Q., Grethe J., Sforza D., MacKenzie-Graham A., Nissanov J., Gustafson C., Toga A. (2007). Accessing a sharing infrastructure with the Mouse BIRN atlasing toolkit (MBAT). In Proceedings of the Society for Neuroscience 37th Annual Meeting, San Diego, CA, USA
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

