Three-dimensional atlas system for mouse and rat brain imaging data
- PMID: 18974799
- PMCID: PMC2525992
- DOI: 10.3389/neuro.11.004.2007
Three-dimensional atlas system for mouse and rat brain imaging data
Abstract
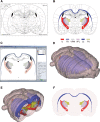
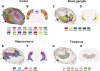
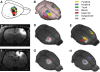
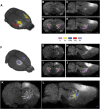
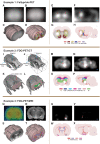
Tomographic neuroimaging techniques allow visualization of functionally and structurally specific signals in the mouse and rat brain. The interpretation of the image data relies on accurate determination of anatomical location, which is frequently obstructed by the lack of structural information in the data sets. Positron emission tomography (PET) generally yields images with low spatial resolution and little structural contrast, and many experimental magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) paradigms give specific signal enhancements but often limited anatomical information. Side-by-side comparison of image data with conventional atlas diagram is hampered by the 2-D format of the atlases, and by the lack of an analytical environment for accumulation of data and integrative analyses. We here present a method for reconstructing 3-D atlases from digital 2-D atlas diagrams, and exemplify 3-D atlas-based analysis of PET and MRI data. The reconstruction procedure is based on two seminal mouse and brain atlases, but is applicable to any stereotaxic atlas. Currently, 30 mouse brain structures and 60 rat brain structures have been reconstructed. To exploit the 3-D atlas models, we have developed a multi-platform atlas tool (available via The Rodent Workbench, http://rbwb.org) which allows combined visualization of experimental image data within the 3-D atlas space together with 3-D viewing and user-defined slicing of selected atlas structures. The tool presented facilitates assignment of location and comparative analysis of signal location in tomographic images with low structural contrast.
Keywords: 3-D reconstruction; atlas; brain; imaging; magnetic resonance imaging; positron emission tomography; stereotaxic; visualization.
Figures

References
-
- Ali A. A., Dale A. M., Badea A., Johnson G. A. (2005). Automated segmentation of neuroanatomical structures in multispectral MR microscopy of the mouse brain. Neuroimage 27, 425–435 - PubMed
-
- Benveniste H., Kim K., Zhang L., Johnson G. A. (2000). Magnetic resonance microscopy of the C57BL mouse brain. Neuroimage 11, 601–611 - PubMed
-
- Boline J. K., MacKenzie-Graham A. A., Shattuck D. W., Yuan H., Anderson S. P., Sforza D. M., Wang J., Williams R. W., Wong W., Martone M. E., Zaslavsky I., Toga A. W.A Digital Atlas and Neuroinformatics Framework for Query and Display of Disparate Data. (2006). Society for Neuroscience 2006. Abstract and itinerary viewer. Program No. 100. 12
-
- Brevik A., Leergaard T. B., Svanevik. M., Bjaalie J. G. (2001). Three dimensional computerised atlas of the rat brain stem precerebellar system: approaches for mapping, visualization, and comparison of spatial distribution data. Anat. Embryol. (Berl.) 204, 319–332 - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

