Adaptive copy number evolution in malaria parasites
- PMID: 18974876
- PMCID: PMC2570623
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000243
Adaptive copy number evolution in malaria parasites
Abstract
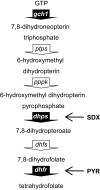
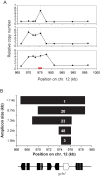
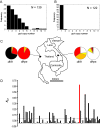
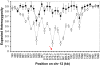
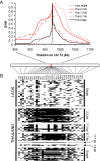
Copy number polymorphism (CNP) is ubiquitous in eukaryotic genomes, but the degree to which this reflects the action of positive selection is poorly understood. The first gene in the Plasmodium folate biosynthesis pathway, GTP-cyclohydrolase I (gch1), shows extensive CNP. We provide compelling evidence that gch1 CNP is an adaptive consequence of selection by antifolate drugs, which target enzymes downstream in this pathway. (1) We compared gch1 CNP in parasites from Thailand (strong historical antifolate selection) with those from neighboring Laos (weak antifolate selection). Two percent of chromosomes had amplified copy number in Laos, while 72% carried multiple (2-11) copies in Thailand, and differentiation exceeded that observed at 73 synonymous SNPs. (2) We found five amplicon types containing one to greater than six genes and spanning 1 to >11 kb, consistent with parallel evolution and strong selection for this gene amplification. gch1 was the only gene occurring in all amplicons suggesting that this locus is the target of selection. (3) We observed reduced microsatellite variation and increased linkage disequilibrium (LD) in a 900-kb region flanking gch1 in parasites from Thailand, consistent with rapid recent spread of chromosomes carrying multiple copies of gch1. (4) We found that parasites bearing dhfr-164L, which causes high-level resistance to antifolate drugs, carry significantly (p = 0.00003) higher copy numbers of gch1 than parasites bearing 164I, indicating functional association between genes located on different chromosomes but linked in the same biochemical pathway. These results demonstrate that CNP at gch1 is adaptive and the associations with dhfr-164L strongly suggest a compensatory function. More generally, these data demonstrate how selection affects multiple enzymes in a single biochemical pathway, and suggest that investigation of structural variation may provide a fast-track to locating genes underlying adaptation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Cooper GM, Nickerson DA, Eichler EE. Mutational and selective effects on copy-number variants in the human genome. Nat Genet. 2007;39:S22–S29. - PubMed
-
- Freeman JL, Perry GH, Feuk L, Redon R, McCarroll SA, et al. Copy number variation: new insights in genome diversity. Genome Res. 2006;16:949–961. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

