Streaking artifacts reduction in four-dimensional cone-beam computed tomography
- PMID: 18975711
- PMCID: PMC2655146
- DOI: 10.1118/1.2977736
Streaking artifacts reduction in four-dimensional cone-beam computed tomography
Abstract
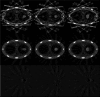
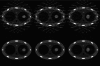
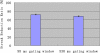
Cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) using an "on-board" x-ray imaging device integrated into a radiation therapy system has recently been made available for patient positioning, target localization, and adaptive treatment planning. One of the challenges for gantry mounted image-guided radiation therapy (IGRT) systems is the slow acquisition of projections for cone-beam CT (CBCT), which makes them sensitive to any patient motion during the scans. Aiming at motion artifact reduction, four-dimensional CBCT (4D CBCT) techniques have been introduced, where a surrogate for the target's motion profile is utilized to sort the cone-beam data by respiratory phase. However, due to the limited gantry rotation speed and limited readout speed of the on-board imager, fewer than 100 projections are available for the image reconstruction at each respiratory phase. Thus, severe undersampling streaking artifacts plague 4D CBCT images. In this paper, the authors propose a simple scheme to significantly reduce the streaking artifacts. In this method, a prior image is first reconstructed using all available projections without gating, in which static structures are well reconstructed while moving objects are blurred. The undersampling streaking artifacts from static structures are estimated from this prior image volume and then can be removed from the phase images using gated reconstruction. The proposed method was validated using numerical simulations, experimental phantom data, and patient data. The fidelity of stationary and moving objects is maintained, while large gains in streak artifact reduction are observed. Using this technique one can reconstruct 4D CBCT datasets using no more projections than are acquired in a 60 s scan. At the same time, a temporal gating window as narrow as 100 ms was utilized. Compared to the conventional 4D CBCT reconstruction, streaking artifacts were reduced by 60% to 70%.
Figures











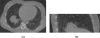
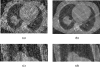


Similar articles
-
High temporal resolution and streak-free four-dimensional cone-beam computed tomography.Phys Med Biol. 2008 Oct 21;53(20):5653-73. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/53/20/006. Epub 2008 Sep 24. Phys Med Biol. 2008. PMID: 18812650 Free PMC article.
-
Slow gantry rotation acquisition technique for on-board four-dimensional digital tomosynthesis.Med Phys. 2010 Feb;37(2):921-33. doi: 10.1118/1.3285291. Med Phys. 2010. PMID: 20229901
-
On-the-fly motion-compensated cone-beam CT using an a priori model of the respiratory motion.Med Phys. 2009 Jun;36(6):2283-96. doi: 10.1118/1.3115691. Med Phys. 2009. PMID: 19610317
-
On-the-fly motion-compensated cone-beam CT using an a priori motion model.Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv. 2008;11(Pt 1):729-36. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-85988-8_87. Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv. 2008. PMID: 18979811
-
Four-dimensional volume-of-interest reconstruction for cone-beam computed tomography-guided radiation therapy.Med Phys. 2011 Oct;38(10):5646-56. doi: 10.1118/1.3634058. Med Phys. 2011. PMID: 21992381 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Image quality in thoracic 4D cone-beam CT: a sensitivity analysis of respiratory signal, binning method, reconstruction algorithm, and projection angular spacing.Med Phys. 2014 Apr;41(4):041912. doi: 10.1118/1.4868510. Med Phys. 2014. PMID: 24694143 Free PMC article.
-
Performance studies of four-dimensional cone beam computed tomography.Phys Med Biol. 2011 Oct 21;56(20):6709-21. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/56/20/013. Epub 2011 Sep 30. Phys Med Biol. 2011. PMID: 21965275 Free PMC article.
-
Motion guided Spatiotemporal Sparsity for high quality 4D-CBCT reconstruction.Sci Rep. 2017 Dec 12;7(1):17461. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-17668-5. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 29234074 Free PMC article.
-
4D micro-CT using fast prospective gating.Phys Med Biol. 2012 Jan 7;57(1):257-71. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/57/1/257. Phys Med Biol. 2012. PMID: 22156062 Free PMC article.
-
A method for volumetric imaging in radiotherapy using single x-ray projection.Med Phys. 2015 May;42(5):2498-509. doi: 10.1118/1.4918577. Med Phys. 2015. PMID: 25979043 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen G.-H., Zambelli J., Nett B. E., Riddell C., Belanger B., and Mistretta C. A., “Design and development of C-arm based cone-beam CT for image-guided interventions: initial results,” Proc. SPIE PSISDG 6142, 614210–614221 (2006).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

