QuantPrime--a flexible tool for reliable high-throughput primer design for quantitative PCR
- PMID: 18976492
- PMCID: PMC2612009
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-9-465
QuantPrime--a flexible tool for reliable high-throughput primer design for quantitative PCR
Abstract
Background: Medium- to large-scale expression profiling using quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) assays are becoming increasingly important in genomics research. A major bottleneck in experiment preparation is the design of specific primer pairs, where researchers have to make several informed choices, often outside their area of expertise. Using currently available primer design tools, several interactive decisions have to be made, resulting in lengthy design processes with varying qualities of the assays.
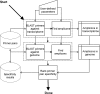
Results: Here we present QuantPrime, an intuitive and user-friendly, fully automated tool for primer pair design in small- to large-scale qPCR analyses. QuantPrime can be used online through the internet http://www.quantprime.de/ or on a local computer after download; it offers design and specificity checking with highly customizable parameters and is ready to use with many publicly available transcriptomes of important higher eukaryotic model organisms and plant crops (currently 295 species in total), while benefiting from exon-intron border and alternative splice variant information in available genome annotations. Experimental results with the model plant Arabidopsis thaliana, the crop Hordeum vulgare and the model green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii show success rates of designed primer pairs exceeding 96%.
Conclusion: QuantPrime constitutes a flexible, fully automated web application for reliable primer design for use in larger qPCR experiments, as proven by experimental data. The flexible framework is also open for simple use in other quantification applications, such as hydrolyzation probe design for qPCR and oligonucleotide probe design for quantitative in situ hybridization. Future suggestions made by users can be easily implemented, thus allowing QuantPrime to be developed into a broad-range platform for the design of RNA expression assays.
Figures





References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

