Kinetic analysis of late steps of eukaryotic translation initiation
- PMID: 18976658
- PMCID: PMC2654283
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmb.2008.10.029
Kinetic analysis of late steps of eukaryotic translation initiation
Abstract
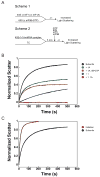
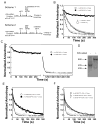
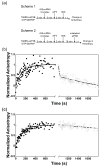
Little is known about the molecular mechanics of the late events of translation initiation in eukaryotes. We present a kinetic dissection of the transition from a preinitiation complex after start codon recognition to the final 80S initiation complex. The resulting framework reveals that eukaryotic initiation factor (eIF)5B actually accelerates the rate of ribosomal subunit joining, and this acceleration is influenced by the conformation of the GTPase active site of the factor mediated by the bound nucleotide. eIF1A accelerates joining through its C-terminal interaction with eIF5B, and eIF1A release from the initiating ribosome, which occurs only after subunit joining, is accelerated by GTP hydrolysis by eIF5B. Following subunit joining, GTP hydrolysis by eIF5B alters the conformation of the final initiation complex and clears a path to promote rapid release of eIF1A. Our data, coupled with previous work, indicate that eIF1A is present on the ribosome throughout the entire initiation process and plays key roles at every stage.
Figures



References
-
- Kapp LD, Lorsch JR. The molecular mechanics of eukaryotic translation. Annu Rev Biochem. 2004;73:657–704. - PubMed
-
- Pestova TV, Lorsch JR, Hellen CUT. The Mechanism of Eukaryotic Translation Initiation in Eukaryotes. In: Mathews MB, Sonenberg N, Hershey JWB, editors. Translational Control in Biology and Medicine. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; Cold Spring Harbor, NY: 2007. pp. 87–128.
-
- Thomas A, Spann W, Van Steeg H, Voorma HO, Benne R. Mode of action of protein synthesis initiation factor eIF-1 from rabbit reticulocytes. FEBS Lett. 1980;116:67–71. - PubMed
-
- Thomas A, Goumans H, Voorma HO, Benne R. The mechanism of action of eukaryotic initiation factor 4C in protein synthesis. Eur J Biochem. 1980;107:39–45. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

