Bacterial heme-transport proteins and their heme-coordination modes
- PMID: 18977196
- PMCID: PMC2683585
- DOI: 10.1016/j.abb.2008.10.013
Bacterial heme-transport proteins and their heme-coordination modes
Abstract
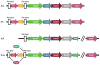
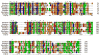
Efficient iron acquisition is critical for an invading microbe's survival and virulence. Most of the iron in mammals is incorporated into heme, which can be plundered by certain bacterial pathogens as a nutritional iron source. Utilization of exogenous heme by bacteria involves the binding of heme or hemoproteins to the cell surface receptors, followed by the transport of heme into cells. Once taken into the cytosol, heme is presented to heme oxygenases where the tetrapyrrole ring is cleaved in order to release the iron. Some Gram-negative bacteria also secrete extracellular heme-binding proteins called hemophores, which function to sequester heme from the environment. The heme-transport genes are often genetically linked as gene clusters under Fur (ferric uptake regulator) regulation. This review discusses the gene clusters and proteins involved in bacterial heme acquisition, transport and processing processes, with special focus on the heme-coordination, protein structures and mechanisms underlying heme-transport.
Figures






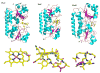
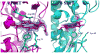


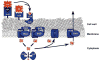

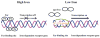
Similar articles
-
[Mechanisms and regulation of iron and heme utilization in Gram-negative bacteria].Postepy Biochem. 2005;51(2):198-208. Postepy Biochem. 2005. PMID: 16209357 Review. Polish.
-
Bacterial iron sources: from siderophores to hemophores.Annu Rev Microbiol. 2004;58:611-47. doi: 10.1146/annurev.micro.58.030603.123811. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15487950 Review.
-
Heme uptake in bacterial pathogens.Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2014 Apr;19:34-41. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2013.12.014. Epub 2014 Jan 4. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2014. PMID: 24780277 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prevalence of Slam-dependent hemophilins in Gram-negative bacteria.J Bacteriol. 2024 Jun 20;206(6):e0002724. doi: 10.1128/jb.00027-24. Epub 2024 May 30. J Bacteriol. 2024. PMID: 38814789 Free PMC article.
-
Heme Uptake and Utilization by Gram-Negative Bacterial Pathogens.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019 Mar 29;9:81. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2019.00081. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30984629 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Iron acquisition system of Sphingobium sp. strain SYK-6, a degrader of lignin-derived aromatic compounds.Sci Rep. 2020 Jul 22;10(1):12177. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-68984-2. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32699224 Free PMC article.
-
Cj1386, an atypical hemin-binding protein, mediates hemin trafficking to KatA in Campylobacter jejuni.J Bacteriol. 2015 Mar;197(5):1002-11. doi: 10.1128/JB.02346-14. Epub 2014 Dec 29. J Bacteriol. 2015. PMID: 25548249 Free PMC article.
-
Hal Is a Bacillus anthracis heme acquisition protein.J Bacteriol. 2012 Oct;194(20):5513-21. doi: 10.1128/JB.00685-12. Epub 2012 Aug 3. J Bacteriol. 2012. PMID: 22865843 Free PMC article.
-
A Sec14-like phosphatidylinositol transfer protein paralog defines a novel class of heme-binding proteins.Elife. 2020 Aug 11;9:e57081. doi: 10.7554/eLife.57081. Elife. 2020. PMID: 32780017 Free PMC article.
-
Handling heme: The mechanisms underlying the movement of heme within and between cells.Free Radic Biol Med. 2019 Mar;133:88-100. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2018.08.005. Epub 2018 Aug 6. Free Radic Biol Med. 2019. PMID: 30092350 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

