Detection of protein S-nitrosylation with the biotin-switch technique
- PMID: 18977293
- PMCID: PMC3120222
- DOI: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2008.09.034
Detection of protein S-nitrosylation with the biotin-switch technique
Abstract
Protein S-nitrosylation, the posttranslational modification of cysteine thiols to form S-nitrosothiols, is a principle mechanism of nitric oxide-based signaling. Studies have demonstrated myriad roles for S-nitrosylation in organisms from bacteria to humans, and recent efforts have greatly advanced our scientific understanding of how this redox-based modification is dynamically regulated during physiological and pathophysiological conditions. The focus of this review is the biotin-switch technique (BST), which has become a mainstay assay for detecting S-nitrosylated proteins in complex biological systems. Potential pitfalls and modern adaptations of the BST are discussed, as are future directions for this assay in the burgeoning field of protein S-nitrosylation.
Figures

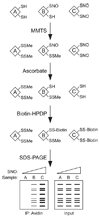

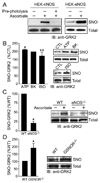
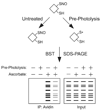
References
-
- Hess DT, Matsumoto A, Kim SO, Marshall HE, Stamler JS. Protein S-nitrosylation: purview and parameters. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2005;6:150–166. - PubMed
-
- Foster MW, McMahon TJ, Stamler JS. S-nitrosylation in health and disease. Trends Mol Med. 2003;9:160–168. - PubMed
-
- Nozik-Grayck E, Whalen EJ, Stamler JS, McMahon TJ, Chitano P, Piantadosi CA. S-nitrosoglutathione inhibits alpha1-adrenergic receptor-mediated vasoconstriction and ligand binding in pulmonary artery. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2006;290:L136–L143. - PubMed
-
- Whalen EJ, Foster MW, Matsumoto A, Ozawa K, Violin JD, Que LG, Nelson CD, Benhar M, Keys JR, Rockman HA, Koch WJ, Daaka Y, Lefkowitz RJ, Stamler JS. Regulation of beta-adrenergic receptor signaling by S-nitrosylation of G-protein-coupled receptor kinase 2. Cell. 2007;129:511–522. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

