BDNF-induced synaptic delivery of AMPAR subunits is differentially dependent on NMDA receptors and requires ERK
- PMID: 18977306
- PMCID: PMC2649981
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nlm.2008.10.002
BDNF-induced synaptic delivery of AMPAR subunits is differentially dependent on NMDA receptors and requires ERK
Abstract
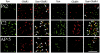
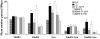
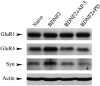
Previous studies using an in vitro model of eyeblink classical conditioning in turtles suggest that increased numbers of synaptic AMPARs supports the acquisition and expression of conditioned responses (CRs). Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and its associated receptor tyrosine kinase, TrkB, is also required for acquisition of CRs. Bath application of BDNF alone induces synaptic delivery of GluR1- and GluR4-containing AMPARs that is blocked by coapplication of the receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor K252a. The molecular mechanisms involved in BDNF-induced AMPAR trafficking remain largely unknown. The aim of this study was to determine whether BDNF-induced synaptic AMPAR incorporation utilizes similar cellular mechanisms as AMPAR trafficking that occurs during in vitro classical conditioning. Using pharmacological blockade and confocal imaging, the results show that synaptic delivery of GluR1 subunits during conditioning or BDNF application does not require activity of NMDARs but is mediated by extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK). In contrast, synaptic delivery of GluR4-containing AMPARs during both conditioning and BDNF application is NMDAR- as well as ERK-dependent. These findings indicate that BDNF application mimics AMPAR trafficking observed during conditioning by activation of some of the same intracellular signaling pathways and suggest that BDNF is a key signal transduction element in postsynaptic events that mediate conditioning.
Figures

References
-
- Anderson CW, Keifer J. Properties of conditioned abducens nerve responses in a highly reduced in vitro brain stem preparation from the turtle. Journal of Neurophysiology. 1999;81:1242–1250. - PubMed
-
- Boehm J, Kang MG, Johnson RC, Esteban J, Huganir RL, Malinow R. Synaptic incorporation of AMPA receptors during LTP is controlled by a PKC phosphorylation site on GluR1. Neuron. 2006;51:213–225. - PubMed
-
- Caldeira MV, Melo CV, Pereira DB, Carvalho R, Correia SS, Backos DS, et al. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor regulates the expression and synaptic delivery of alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole propionic acid receptor subunits in hippocampal neurons. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2007;282:12619–12628. - PubMed
-
- Carlezon WA, Jr., Duman RS, Nestler EJ. The many faces of CREB. Trends in Neuroscience. 2005;28:436–445. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

