miR-296 regulates growth factor receptor overexpression in angiogenic endothelial cells
- PMID: 18977327
- PMCID: PMC2597164
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccr.2008.10.005
miR-296 regulates growth factor receptor overexpression in angiogenic endothelial cells
Abstract
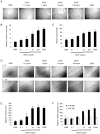
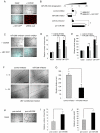
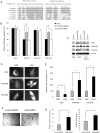
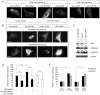
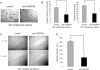
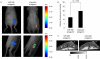
A key step in angiogenesis is the upregulation of growth factor receptors on endothelial cells. Here, we demonstrate that a small regulatory microRNA, miR-296, has a major role in this process. Glioma cells and angiogenic growth factors elevate the level of miR-296 in primary human brain microvascular endothelial cells in culture. The miR-296 level is also elevated in primary tumor endothelial cells isolated from human brain tumors compared to normal brain endothelial cells. Growth factor-induced miR-296 contributes significantly to angiogenesis by directly targeting the hepatocyte growth factor-regulated tyrosine kinase substrate (HGS) mRNA, leading to decreased levels of HGS and thereby reducing HGS-mediated degradation of the growth factor receptors VEGFR2 and PDGFRbeta. Furthermore, inhibition of miR-296 with antagomirs reduces angiogenesis in tumor xenografts in vivo.
Figures


References
-
- Ambros V. The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature. 2004;431:350–355. - PubMed
-
- Bache KG, Raiborg C, Mehlum A, Stenmark H. STAM and Hrs are subunits of a multivalent ubiquitin-binding complex on early endosomes. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:12513–12521. - PubMed
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–297. - PubMed
-
- Brem S, Cotran R, Folkman J. Tumor angiogenesis: a quantitative method for histologic grading. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1972;48:347–356. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

