Inactivation of the CYLD deubiquitinase by HPV E6 mediates hypoxia-induced NF-kappaB activation
- PMID: 18977328
- PMCID: PMC2651888
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccr.2008.10.007
Inactivation of the CYLD deubiquitinase by HPV E6 mediates hypoxia-induced NF-kappaB activation
Abstract
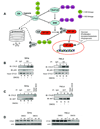
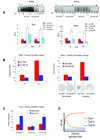
The biochemical mechanisms that underlie hypoxia-induced NF-kappaB activity have remained largely undefined. Here, we find that prolonged hypoxia-induced NF-kappaB activation is restricted to cancer cell lines infected with high-risk human papillomavirus (HPV) serotypes. The HPV-encoded E6 protein is necessary and sufficient for prolonged hypoxia-induced NF-kappaB activation in these systems. The molecular target of E6 in the NF-kappaB pathway is the CYLD lysine 63 (K63) deubiquitinase, a negative regulator of the NF-kappaB pathway. Specifically, hypoxia stimulates E6-mediated ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation of CYLD. Given the established role of NF-kappaB in human carcinogenesis, these findings provide a potential molecular/viral link between hypoxia and the adverse clinical outcomes observed in HPV-associated malignancies.
Figures
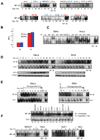
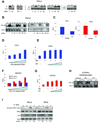
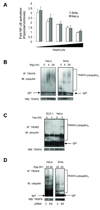
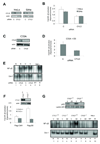


References
-
- Basseres DS, Baldwin AS. Nuclear factor-kappaB and inhibitor of kappaB kinase pathways in oncogenic initiation and progression. Oncogene. 2006;25:6817–6830. - PubMed
-
- Brummelkamp TR, Nijman SM, Dirac AM, Bernards R. Loss of the cylindromatosis tumour suppressor inhibits apoptosis by activating NF-kappaB. Nature. 2003;424:797–801. - PubMed
-
- Butz K, Ristriani T, Hengstermann A, Denk C, Scheffner M, Hoppe-Seyler F. siRNA targeting of the viral E6 oncogene efficiently kills human papillomavirus-positive cancer cells. Oncogene. 2003;22:5938–5945. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

