Overexpression of interleukin-1beta induces gastric inflammation and cancer and mobilizes myeloid-derived suppressor cells in mice
- PMID: 18977329
- PMCID: PMC2586894
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccr.2008.10.011
Overexpression of interleukin-1beta induces gastric inflammation and cancer and mobilizes myeloid-derived suppressor cells in mice
Erratum in
- Cancer Cell. 2008 Dec 9;14(6):494
- Cancer Cell. 2011 Jan 18;19(1):154
Abstract
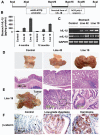
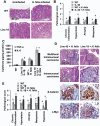
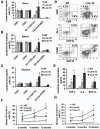
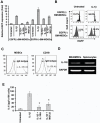
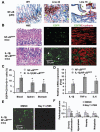
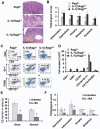
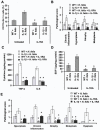
Polymorphisms of interleukin-1beta (IL-1beta) are associated with an increased risk of solid malignancies. Here, we show that stomach-specific expression of human IL-1beta in transgenic mice leads to spontaneous gastric inflammation and cancer that correlate with early recruitment of myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) to the stomach. IL-1beta activates MDSCs in vitro and in vivo through an IL-1RI/NF-kappaB pathway. IL-1beta transgenic mice deficient in T and B lymphocytes develop gastric dysplasia accompanied by a marked increase in MDSCs in the stomach. Antagonism of IL-1 receptor signaling inhibits the development of gastric preneoplasia and suppresses MDSC mobilization. These results demonstrate that pathologic elevation of a single proinflammatory cytokine may be sufficient to induce neoplasia and provide a direct link between IL-1beta, MDSCs, and carcinogenesis.
Figures
References
-
- Almand B, Clark JI, Nikitina E, van Beynen J, English NR, Knight SC, Carbone DP, Gabrilovich DI. Increased production of immature myeloid cells in cancer patients: a mechanism of immunosuppression in cancer. J Immunol. 2001;166:678–689. - PubMed
-
- Arend WP. The balance between IL-1 and IL-1Ra in disease. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2002;13:323–340. - PubMed
-
- Balkwill F. TNF-alpha in promotion and progression of cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2006;25:409–416. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

