Adaptation to chronic hypoxia involves immune cell invasion and increased expression of inflammatory cytokines in rat carotid body
- PMID: 18978039
- PMCID: PMC2643993
- DOI: 10.1152/ajplung.90383.2008
Adaptation to chronic hypoxia involves immune cell invasion and increased expression of inflammatory cytokines in rat carotid body
Abstract
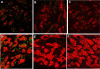
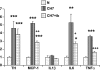
Exposure to chronic hypoxia (CH; 3-28 days at 380 Torr) induces adaptation in mammalian carotid body such that following CH an acute hypoxic challenge elicits an abnormally large increase in carotid sinus nerve impulse activity. The current study examines the hypothesis that CH initiates an immune response in the carotid body and that chemoreceptor hyperexcitability is dependent on the expression and action of inflammatory cytokines. CH resulted in a robust invasion of ED1(+) macrophages, which peaked on day 3 of exposure. Gene expression of proinflammatory cytokines, IL-1beta, TNFalpha, and the chemokine, monocyte chemoattractant protein-1, was increased >2-fold after 1 day of hypoxia followed by a >2-fold increase in IL-6 on day 3. After 28 days of CH, IL-6 remained elevated >5-fold, whereas expression of other cytokines recovered to normal levels. Cytokine expression was not restricted to immune cells. Studies of cultured type I cells harvested following 1 day of in vivo hypoxia showed elevated transcript levels of inflammatory cytokines. In situ hybridization studies confirmed expression of IL-6 in type I cells and also showed that CH induces IL-6 expression in supporting type II cells. Concurrent treatment of CH rats with anti-inflammatory drugs (ibuprofen or dexamethasone) blocked immune cell invasion and severely reduced CH-induced cytokine expression in carotid body. Drug treatment also blocked the development of chemoreceptor hypersensitivity in CH animals. Our findings indicate that chemoreceptor adaptation involves novel neuroimmune mechanisms, which may alter the functional phenotypes of type I cells and chemoafferent neurons.
Figures

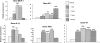

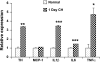


Comment in
-
Adaptation to chronic hypoxia involves immune cell invasion and increased expression of inflammatory cytokines in rat carotid body.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2009 Feb;296(2):L156-7. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.90597.2008. Epub 2008 Dec 12. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19074555 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Chronic hypoxia-induced acid-sensitive ion channel expression in chemoafferent neurons contributes to chemoreceptor hypersensitivity.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2011 Dec;301(6):L985-92. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00132.2011. Epub 2011 Sep 2. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21890510 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of endothelin receptor antagonist bosentan on chronic hypoxia-induced inflammation and chemoafferent neuron adaptation in rat carotid body.High Alt Med Biol. 2012 Sep;13(3):209-16. doi: 10.1089/ham.2012.1011. High Alt Med Biol. 2012. PMID: 22994521 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic intermittent hypoxia induces local inflammation of the rat carotid body via functional upregulation of proinflammatory cytokine pathways.Histochem Cell Biol. 2012 Mar;137(3):303-17. doi: 10.1007/s00418-011-0900-5. Epub 2011 Dec 21. Histochem Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22187044 Free PMC article.
-
Expressions of angiotensin and cytokine receptors in the paracrine signaling of the carotid body in hypoxia and sleep apnea.Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2015 Apr;209:6-12. doi: 10.1016/j.resp.2014.09.014. Epub 2014 Oct 3. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2015. PMID: 25266394 Review.
-
A chronic pain: inflammation-dependent chemoreceptor adaptation in rat carotid body.Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2011 Sep 30;178(3):362-9. doi: 10.1016/j.resp.2011.03.006. Epub 2011 Mar 17. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2011. PMID: 21397054 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Sustained exposure to cytokines and hypoxia enhances excitability of oxygen-sensitive type I cells in rat carotid body: correlation with the expression of HIF-1α protein and adrenomedullin.High Alt Med Biol. 2013 Mar;14(1):53-60. doi: 10.1089/ham.2012.1054. High Alt Med Biol. 2013. PMID: 23537261 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence and Characteristics of Central Compared to Obstructive Sleep Apnea: Analyses from the Sleep Heart Health Study Cohort.Sleep. 2016 Jul 1;39(7):1353-9. doi: 10.5665/sleep.5962. Sleep. 2016. PMID: 27166235 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogenic roles of the carotid body inflammation in sleep apnea.Mediators Inflamm. 2014;2014:354279. doi: 10.1155/2014/354279. Epub 2014 Sep 7. Mediators Inflamm. 2014. PMID: 25276055 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypoxic Signaling Pathways in Carotid Body Tumors.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Jan 30;16(3):584. doi: 10.3390/cancers16030584. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38339335 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulation of chronic hypoxia-induced chemoreceptor hypersensitivity by NADPH oxidase subunits in rat carotid body.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2010 May;108(5):1304-10. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00766.2009. Epub 2010 Feb 25. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2010. PMID: 20185631 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bee D, Pallot DJ, Barer GR. Division of type I and endothelial cells in the hypoxic rat carotid body. Acta Anat (Basel) 126: 226–229, 1986. - PubMed
-
- Bisgard GE Carotid body mechanisms in acclimatization to hypoxia. Respir Physiol 121: 237–246, 2000. - PubMed
-
- Chen J, He L, Dinger B, Stensaas L, Fidone S. Role of endothelin and endothelin A-type receptor in physiological adaptation of the carotid body during chronic hypoxia. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 282: L1314–L1323, 2002. - PubMed
-
- Chen J, He L, Dinger B, Stensaas L, Fidone S. Chronic hypoxia upregulates connexin43 expression in rat carotid body and petrosal ganglion. J Appl Physiol 92: 1480–1486, 2002. - PubMed
-
- Chen J, He L, Liu X, Dinger B, Stensaas L, Fidone S. Effect of the endothelin receptor antagonist bosentan on chronic hypoxia-induced morphological and physiological changes in rat carotid body. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 292: L1257–L1262, 2007. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

