Expression and physiological relevance of Agrobacterium tumefaciens phosphatidylcholine biosynthesis genes
- PMID: 18978052
- PMCID: PMC2612428
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.01183-08
Expression and physiological relevance of Agrobacterium tumefaciens phosphatidylcholine biosynthesis genes
Abstract
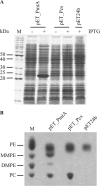
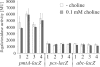
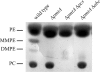
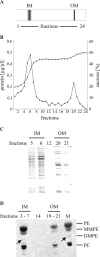
Phosphatidylcholine (PC), or lecithin, is the major phospholipid in eukaryotic membranes, whereas only 10% of all bacteria are predicted to synthesize PC. In Rhizobiaceae, including the phytopathogenic bacterium Agrobacterium tumefaciens, PC is essential for the establishment of a successful host-microbe interaction. A. tumefaciens produces PC via two alternative pathways, the methylation pathway and the Pcs pathway. The responsible genes, pmtA (coding for a phospholipid N-methyltransferase) and pcs (coding for a PC synthase), are located on the circular chromosome of A. tumefaciens C58. Recombinant expression of pmtA and pcs in Escherichia coli revealed that the individual proteins carry out the annotated enzyme functions. Both genes and a putative ABC transporter operon downstream of PC are constitutively expressed in A. tumefaciens. The amount of PC in A. tumefaciens membranes reaches around 23% of total membrane lipids. We show that PC is distributed in both the inner and outer membranes. Loss of PC results in reduced motility and increased biofilm formation, two processes known to be involved in virulence. Our work documents the critical importance of membrane lipid homeostasis for diverse cellular processes in A. tumefaciens.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Membrane lipids in Agrobacterium tumefaciens: biosynthetic pathways and importance for pathogenesis.Front Plant Sci. 2014 Mar 26;5:109. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2014.00109. eCollection 2014. Front Plant Sci. 2014. PMID: 24723930 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Virulence of Agrobacterium tumefaciens requires phosphatidylcholine in the bacterial membrane.Mol Microbiol. 2006 Nov;62(3):906-15. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2006.05425.x. Epub 2006 Sep 29. Mol Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 17010159
-
Phosphatidylcholine biosynthesis and function in bacteria.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Mar;1831(3):503-13. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2012.08.009. Epub 2012 Aug 19. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 22922101 Review.
-
Membrane-binding mechanism of a bacterial phospholipid N-methyltransferase.Mol Microbiol. 2015 Jan;95(2):313-31. doi: 10.1111/mmi.12870. Epub 2014 Dec 19. Mol Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25403021
-
Enzymatic properties and substrate specificity of a bacterial phosphatidylcholine synthase.FEBS J. 2014 Aug;281(15):3523-41. doi: 10.1111/febs.12877. Epub 2014 Jul 14. FEBS J. 2014. PMID: 24931117
Cited by
-
The RNase YbeY Is Vital for Ribosome Maturation, Stress Resistance, and Virulence of the Natural Genetic Engineer Agrobacterium tumefaciens.J Bacteriol. 2019 May 8;201(11):e00730-18. doi: 10.1128/JB.00730-18. Print 2019 Jun 1. J Bacteriol. 2019. PMID: 30885931 Free PMC article.
-
Choline uptake in Agrobacterium tumefaciens by the high-affinity ChoXWV transporter.J Bacteriol. 2011 Oct;193(19):5119-29. doi: 10.1128/JB.05421-11. Epub 2011 Jul 29. J Bacteriol. 2011. PMID: 21803998 Free PMC article.
-
Genome sequence of Ensifer adhaerens OV14 provides insights into its ability as a novel vector for the genetic transformation of plant genomes.BMC Genomics. 2014 Apr 7;15:268. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-268. BMC Genomics. 2014. PMID: 24708309 Free PMC article.
-
Membrane lipids in Agrobacterium tumefaciens: biosynthetic pathways and importance for pathogenesis.Front Plant Sci. 2014 Mar 26;5:109. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2014.00109. eCollection 2014. Front Plant Sci. 2014. PMID: 24723930 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative genomic analysis between newly sequenced Brucella suis Vaccine Strain S2 and the Virulent Brucella suis Strain 1330.BMC Genomics. 2016 Sep 20;17(1):741. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-3076-5. BMC Genomics. 2016. PMID: 27645563 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bligh, E. G., and W. J. Dyer. 1959. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can. J. Biochem. Physiol. 37911-917. - PubMed
-
- Canty, D. J., and S. H. Zeisel. 1994. Lecithin and choline in human health and disease. Nutr. Rev. 52327-339. - PubMed
-
- Chesnokova, O., J. B. Coutinho, I. H. Khan, M. S. Mikhail, and C. I. Kado. 1997. Characterization of flagella genes of Agrobacterium tumefaciens, and the effect of a bald strain on virulence. Mol. Microbiol. 23579-590. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

