Detecting microRNA binding and siRNA off-target effects from expression data
- PMID: 18978784
- PMCID: PMC2635553
- DOI: 10.1038/nmeth.1267
Detecting microRNA binding and siRNA off-target effects from expression data
Abstract
Sylamer is a method for detecting microRNA target and small interfering RNA off-target signals in 3' untranslated regions from a ranked gene list, sorted from upregulated to downregulated, after a microRNA perturbation or RNA interference experiment. The output is a landscape plot that tracks occurrence biases using hypergeometric P-values for all words across the gene ranking. We demonstrated the utility, speed and accuracy of this approach on several datasets.
Figures
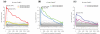
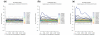
References
-
- Lewis BP, Burge CB, Bartel DP. Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell. 2005;120:15–20. - PubMed
-
- Farh KK, et al. The widespread impact of mammalian MicroRNAs on mRNA repression and evolution. Science. 2005;310:1817–1821. - PubMed
-
- Giraldez AJ, et al. Zebrafish MiR-430 promotes deadenylation and clearance of maternal mRNAs. Science. 2006;312:75–79. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

