Redox warfare between airway epithelial cells and Pseudomonas: dual oxidase versus pyocyanin
- PMID: 18979077
- PMCID: PMC2776630
- DOI: 10.1007/s12026-008-8071-8
Redox warfare between airway epithelial cells and Pseudomonas: dual oxidase versus pyocyanin
Abstract
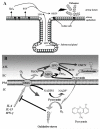
The importance of reactive oxygen species-dependent microbial killing by the phagocytic cell NADPH oxidase has been appreciated for some time, although only recently has an appreciation developed for the partnership of lactoperoxidase with related dual oxidases (Duox) within secretions of the airway surface layer. This system produces mild oxidants designed for extracellular killing that are effective against several airway pathogens, including Staphylococcus aureus, Burkholderia cepacia, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Establishment of chronic pseudomonas infections involves adaptations to resist oxidant-dependent killing by expression of a redox-active virulence factor, pyocyanin, that competitively inhibits epithelial Duox activity by consuming intracellular NADPH and producing superoxide, thereby inflicting oxidative stress on the host.
Figures
References
-
- Leto TL. The respiratory burst oxidase. In: Gallin JI, Snyderman R, editors. Inflammation. Basic principles and clinical correlates. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins; Philedelphia: 1999. pp. 769–786.
-
- Segal BH, Leto TL, Gallin JI, Malech HL, Holland SM. Genetic, biochemical, and clinical features of chronic granulomatous disease. Medicine (Baltimore) 2000;79:170–200. - PubMed
-
- Finkel T. Reactive oxygen species and signal transduction. IUBMB Life. 2001;52:3–6. - PubMed
-
- Geiszt M, Leto TL. The Nox family of NAD(P)H oxidases: host defense and beyond. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:51715–51718. - PubMed
-
- Lambeth JD. NOX enzymes and the biology of reactive oxygen. Nat Rev Immunol. 2004;4:181–189. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

