Genome-wide association scan of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder
- PMID: 18980221
- PMCID: PMC2831205
- DOI: 10.1002/ajmg.b.30866
Genome-wide association scan of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder
Abstract
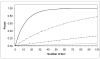
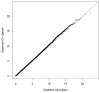
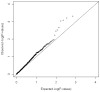
Results of behavioral genetic and molecular genetic studies have converged to suggest that genes substantially contribute to the development of attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), a common disorder with an onset in childhood. Yet, despite numerous linkage and candidate gene studies, strongly consistent and replicable association has eluded detection. To search for ADHD susceptibility genes, we genotyped approximately 600,000 SNPs in 958 ADHD affected family trios. After cleaning the data, we analyzed 438,784 SNPs in 2,803 individuals comprising 909 complete trios using ADHD diagnosis as phenotype. We present the initial TDT findings as well as considerations for cleaning family-based TDT data. None of the SNP association tests achieved genome-wide significance, indicating that larger samples may be required to identify risk loci for ADHD. We additionally identify a systemic bias in family-based association, and suggest that variable missing genotype rates may be the source of this bias.
Copyright 2008 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Altshuler D, Daly M. Guilt beyond a reasonable doubt. Nat Genet. 2007;39(7):813–5. - PubMed
-
- American Psychiatric A. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders: DSM-III-R. Washington, D.C: American Psychiatric Association; 1987. p. 567. %7 3rd-Revised p.
-
- Arcos-Burgos M, Castellanos FX, Pineda D, Lopera F, David Palacio J, Guillermo Palacio L, Rapoport JL, Berg K, Bailey-Wilson JE, Muenke M. Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in a population isolate: linkage to Loci at 4q13.2, 5q33.3, 11q22, and 17p11. Am J Hum Genet. 2004;75(6):998–1014. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Asherson P, Zhou K, Anney RJ, Franke B, Buitelaar J, Ebstein R, Gill M, Altink M, Arnold R, Boer F, et al. A high-density SNP linkage scan with 142 combined subtype ADHD sib pairs identifies linkage regions on chromosomes 9 and 16. Mol Psychiatry. 2008;13(5):514–21. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

