Systematic review and meta-analysis of ovarian cancers: estimation of microsatellite-high frequency and characterization of mismatch repair deficient tumor histology
- PMID: 18980979
- PMCID: PMC2655731
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-1387
Systematic review and meta-analysis of ovarian cancers: estimation of microsatellite-high frequency and characterization of mismatch repair deficient tumor histology
Abstract
Purpose: A meta-analytic approach was used to estimate the frequency of: (a) microsatellite instability-high (MSI-H) phenotype in unselected ovarian cancers and (b) various histologic subtypes of mismatch repair (MMR)-deficient epithelial ovarian cancers.
Methods: A systematic search of the Medline electronic database was conducted to identify articles published between January 1, 1966, and December 31, 2007, that examined MMR deficiency in ovarian cancers. Data were extracted on the study population, sample size, MSI-H frequency, and histology of MMR-deficient ovarian tumors.
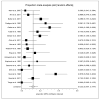
Results: The pooled proportion of MSI-H ovarian cancers was 0.12 [95% confidence interval (CI), 0.08-0.17] from 18 studies with 977 cases. The proportion of histologic subtypes in the pooled analysis from 15 studies with 159 cases was serous at 0.32 (95% CI, 0.20-0.44), mucinous at 0.19 (95% CI, 0.12-0.27), endometrioid at 0.29 (95% CI, 0.22-0.36), clear cell at 0.18 (95% CI, 0.09-0.28), and mixed at 0.24 (95% CI, 0.07-0.47). There was significant heterogeneity between studies.
Conclusions: The frequency of the MSI-H phenotype in unselected ovarian cancers approximates 12%. MMR-deficient ovarian cancers also seem to be characterized by an overrepresentation of nonserous histologic subtypes. Knowledge of histologic subtype may aid clinicians in identifying the relatively large proportion of ovarian cancers due to MMR defects; such knowledge has potential implications for medical management.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Figures
References
-
- American Cancer Society. Cancer facts and figures 2006. Atlanta: American Cancer Society; 2006.
-
- Boyd J, Rubin SC. Hereditary ovarian cancer: molecular genetics and clinical implications. Gynecol Oncol. 1997;64:196–206. - PubMed
-
- Bewtra C, Watson P, Conway T, Read-Hippee C, Lynch HT. Hereditary ovarian cancer: a clinicopathological study. Int J Gynecol Pathol. 1992;11:180–7. - PubMed
-
- Akiyama Y, Sato H, Yamada T, et al. Germ-line mutation of the hMSH6/GTBP gene in an atypical hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer kindred. Cancer Res. 1997;57:3920–3. - PubMed
-
- Bronner CE, Baker SM, Morrison PT, et al. Mutation in the DNA mismatch repair gene homologue hMLH1 is associated with hereditary non-polyposis colon cancer. Nature. 1994;368:258–61. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical