Resveratrol and 4-hydroxynonenal act in concert to increase glutamate cysteine ligase expression and glutathione in human bronchial epithelial cells
- PMID: 18983812
- PMCID: PMC2692270
- DOI: 10.1016/j.abb.2008.10.020
Resveratrol and 4-hydroxynonenal act in concert to increase glutamate cysteine ligase expression and glutathione in human bronchial epithelial cells
Abstract
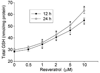
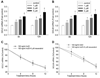
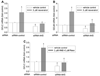
Resveratrol has been shown to protect against oxidative stress through modulating antioxidant capacity. In this study, we investigated resveratrol-mediated induction of glutathione (GSH) and glutamate cysteine ligase (GCL), and the combined effect of resveratrol and 4-hydroxynonenal (HNE) on GSH synthesis in cultured HBE1 human bronchial epithelial cells. Resveratrol increased GSH and the mRNA contents of both the catalytic (GCLC) and modulatory subunit (GCLM) of GCL. Combined HNE and resveratrol treatment increased GSH content and GCL mRNAs to a greater extent than either compound did alone. Compared to individual agent, combining exposure to HNE and resveratrol also showed more protection against cell death caused by oxidative stress. These effects of combined exposure were additive rather than synergistic. In addition, Nrf2 silencing significantly decreased the combined effect of HNE and resveratrol on GCL induction. Our data suggest that resveratrol increases GSH and GCL gene expression and that there is an additive effect on GSH synthesis between resveratrol and HNE. The results also reveal that Nrf2-EpRE signaling was involved in the combined effects.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

