How a cyanobacterium tells time
- PMID: 18983934
- PMCID: PMC2692899
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mib.2008.10.003
How a cyanobacterium tells time
Abstract
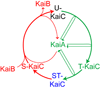
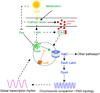
The cyanobacterium Synechococcus elongatus builds a circadian clock on an oscillator composed of three proteins, KaiA, KaiB, and KaiC, which can recapitulate a circadian rhythm of KaiC phosphorylation in vitro. The molecular structures of all three proteins are known, and the phosphorylation steps of KaiC, the interaction dynamics among the three Kai proteins, and a weak ATPase activity of KaiC have all been characterized. An input pathway of redox-sensitive proteins uses photosynthetic function to relay light/dark information to the oscillator, and signal transduction proteins of well-known families broadcast temporal information to the genome, where global changes in transcription and a compaction of the chromosome are clock regulated.
Figures
References
-
- Ishiura M, Kutsuna S, Aoki S, Iwasaki H, Andersson CR, Tanabe A, Golden SS, Johnson CH, Kondo T. Expression of a gene cluster kaiABC as a circadian feedback process in cyanobacteria. Science. 1998;281:1519–1523. - PubMed
-
- Nakajima M, Imai K, Ito H, Nishiwaki T, Murayama Y, Iwasaki H, Oyama T, Kondo T. Reconstitution of circadian oscillation of cyanobacterial KaiC phosphorylation in vitro. Science. 2005;308:414–415. - PubMed
-
-
Nishiwaki T, Satomi Y, Kitayama Y, Terauchi K, Kiyohara R, Takao T, Kondo T. A sequential program of dual phosphorylation of KaiC as a basis for circadian rhythm in cyanobacteria. Embo J. 2007;26:4029–4037. The authors successfully characterized the ordered steps of KaiC phosphorylation and the default KaiC activity at each step. Using KaiC phosphomimetics, they were also able to show that KaiC phosphorylation at S431 is critical for interaction among the three Kai proteins.
-
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

