Nf1-dependent tumors require a microenvironment containing Nf1+/-- and c-kit-dependent bone marrow
- PMID: 18984156
- PMCID: PMC2788814
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.08.041
Nf1-dependent tumors require a microenvironment containing Nf1+/-- and c-kit-dependent bone marrow
Abstract
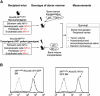
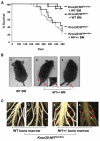
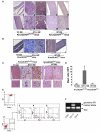
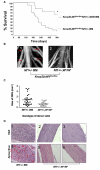
Interactions between tumorigenic cells and their surrounding microenvironment are critical for tumor progression yet remain incompletely understood. Germline mutations in the NF1 tumor suppressor gene cause neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1), a common genetic disorder characterized by complex tumors called neurofibromas. Genetic studies indicate that biallelic loss of Nf1 is required in the tumorigenic cell of origin in the embryonic Schwann cell lineage. However, in the physiologic state, Schwann cell loss of heterozygosity is not sufficient for neurofibroma formation and Nf1 haploinsufficiency in at least one additional nonneoplastic lineage is required for tumor progression. Here, we establish that Nf1 heterozygosity of bone marrow-derived cells in the tumor microenvironment is sufficient to allow neurofibroma progression in the context of Schwann cell Nf1 deficiency. Further, genetic or pharmacologic attenuation of c-kit signaling in Nf1+/- hematopoietic cells diminishes neurofibroma initiation and progression. Finally, these studies implicate mast cells as critical mediators of tumor initiation.
Figures
Comment in
-
It takes a (dysfunctional) village to raise a tumor.Cell. 2008 Oct 31;135(3):408-10. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.10.009. Cell. 2008. PMID: 18984150 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bhowmick NA, Chytil A, Plieth D, Gorska AE, Dumont N, Shappell S, Washington MK, Neilson EG, Moses HL. TGF-beta signaling in fibroblasts modulates the oncogenic potential of adjacent epithelia. Science. 2004;303:848–851. - PubMed
-
- Boesiger J, Tsai M, Maurer M, Yamaguchi M, Brown LF, Claffey KP, Dvorak HF, Galli SJ. Mast cells can secrete vascular permeability factor/ vascular endothelial cell growth factor and exhibit enhanced release after immunoglobulin E-dependent upregulation of fc epsilon receptor I expression. J. Exp. Med. 1998;188:1135–1145. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bollag G, McCormick F. Differential regulation of rasGAP and neurofibromatosis gene product activities. Nature. 1991;351:576–579. - PubMed
-
- Chang T, McGrae JD, Jr., Hashimoto K. Ultrastructural study of two patients with both piebaldism and neurofibromatosis 1. Pediatr. Dermatol. 1993;10:224–234. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

