The histone demethylases JMJD1A and JMJD2B are transcriptional targets of hypoxia-inducible factor HIF
- PMID: 18984585
- PMCID: PMC2662309
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M804578200
The histone demethylases JMJD1A and JMJD2B are transcriptional targets of hypoxia-inducible factor HIF
Abstract
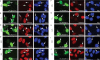
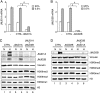
Posttranslational histone modifications serve to store epigenetic information and control both nucleosome assembly and recruitment of non-histone proteins. Histone methylation occurs on arginine and lysine residues and is involved in the regulation of gene transcription. A dynamic control of these modifications is exerted by histone methyltransferases and the recently discovered histone demethylases. Here we show that the hypoxia-inducible factor HIF-1alpha binds to specific recognition sites in the genes encoding the jumonji family histone demethylases JMJD1A and JMJD2B and induces their expression. Accordingly, hypoxic cells express elevated levels of JMJD1A and JMJD2B mRNA and protein. Furthermore, we find increased expression of JMJD1A and JMJD2B in renal cancer cells that have lost the von Hippel Lindau tumor suppressor protein VHL and therefore display a deregulated expression of hypoxia-inducible factor. Studies on ectopically expressed JMJD1A and JMJD2B indicate that both proteins retain their histone lysine demethylase activity in hypoxia and thereby might impact the hypoxic gene expression program.
Figures
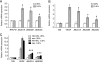
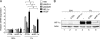



References
-
- Bannister, A. J., Zegerman, P., Partridge, J. F., Miska, E. A., Thomas, J. O., Allshire, R. C., and Kouzarides, T. (2001) Nature 410 120-124 - PubMed
-
- Lachner, M., O'Carroll, D., Rea, S., Mechtler, K., and Jenuwein, T. (2001) Nature 410 116-120 - PubMed
-
- Wysocka, J., Swigut, T., Xiao, H., Milne, T. A., Kwon, S. Y., Landry, J., Kauer, M., Tackett, A. J., Chait, B. T., Badenhorst, P., Wu, C., and Allis, C. D. (2006) Nature 442 86-90 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

