Probing Membrane Insertion Activity of Antimicrobial Polymers via Coarse-grain Molecular Dynamics
- PMID: 18985168
- PMCID: PMC2577386
- DOI: 10.1021/ct050298p
Probing Membrane Insertion Activity of Antimicrobial Polymers via Coarse-grain Molecular Dynamics
Abstract
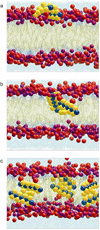
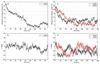
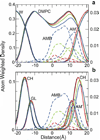
Knowledge of the mechanism of action of antimicrobial agents is crucial for the development of new compounds to combat microbial pathogens. To this end, computational studies on the interaction of known membrane-active antimicrobial polymers with phospholipid bilayers reveal spontaneous membrane insertion and cooperative action at low and high concentrations, respectively. In late-stage attack, antimicrobials cross the membrane core and occasionally align to provide a stepping-stone pathway for water permeation; this suggests a possible new mode of action that does not depend on pore formation for transport to and across the inner leaflet. The computations rationalize the observed activity of a new class of antimicrobial compounds.
Figures
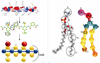


References
-
- Cohen ML. Nature. 2000;406:762–767. - PubMed
-
- Anderson RM. Nature Med. 1999;5:147–149. - PubMed
-
- Niller E. Nature Biotechnol. 2002;20:21–25. - PubMed
-
- Fernandez-Lopez S, Kim HS, Choi EC, Delgado M, Granja JR, Khasanov A, Kraehenbuehl K, Long G, Weinberger DA, Wilcoxen KM, Ghadiri MR. Nature. 2001;412:452–455. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
